Will a 20-Year-Old Felony Affect My Job Application?

What Is a Background Check?
A background check is a verification process conducted by employers, landlords, or organizations to gather information about an individual’s past. These checks are commonly used in hiring, renting, or evaluating a person’s eligibility for specific roles or opportunities. They provide insights into various aspects of a person’s history, including their criminal record, employment history, education, credit, and more.
Background checks are essential for:
- Employment: To assess whether a candidate is qualified and trustworthy for a role.
- Tenant Screening: To determine if a tenant has a reliable rental and payment history.
- Licensing and Certification: For professions requiring clean records (e.g., healthcare, finance).
- Safety and Security: To minimize risks in workplaces, schools, and other sensitive environments.
By identifying potential red flags, background checks help organizations make informed decisions and protect their interests.
How Do Background Checks Work?
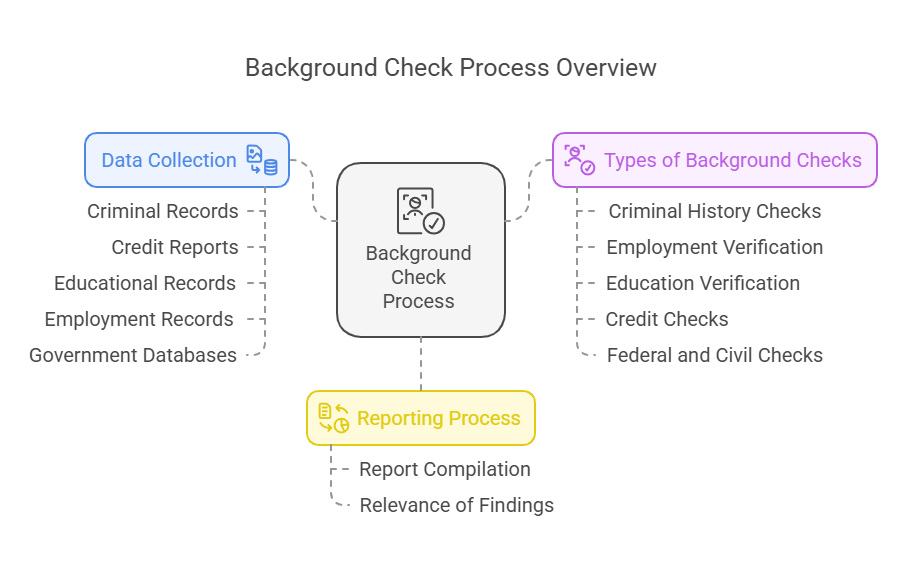
Background checks rely on databases and public records to compile information. Here’s a breakdown of how they work:
- Data Collection: Background check services access multiple sources:
- Criminal records: Federal, state, and local court systems.
- Credit reports: From credit bureaus like Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion.
- Educational records: To verify degrees and certifications.
- Employment records: To confirm work history and references.
- Government databases: For security and compliance checks.
- Types of Background Checks:
- Criminal history checks: Focus on felonies, misdemeanors, and arrests.
- Employment verification: Confirms job titles, employers, and dates of employment.
- Education verification: Validates degrees, certifications, and institutions attended.
- Credit checks: Reviews financial stability and creditworthiness.
- Federal and civil checks: Include federal crimes, lawsuits, and liens.
- Reporting Process: The gathered information is compiled into a report that highlights relevant findings based on the requester’s needs. The depth of the report varies depending on the type of check conducted.
What Are Felonies?
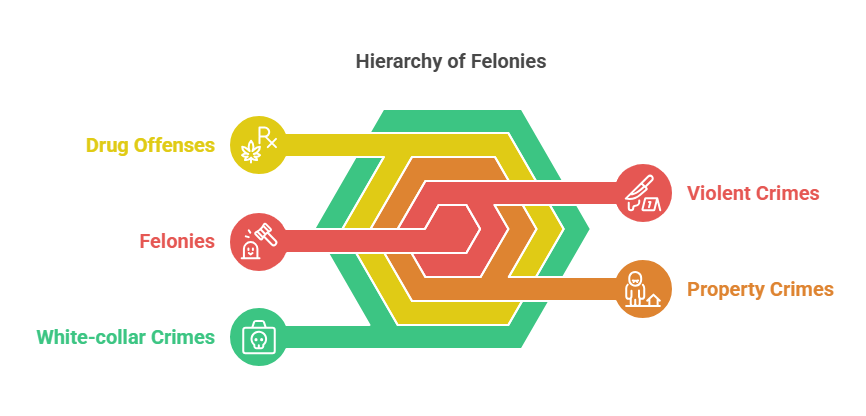
Felonies are serious crimes that typically carry severe penalties, including imprisonment for more than one year, significant fines, or both. Felonies are classified as higher-level offenses compared to misdemeanors and are often associated with long-term consequences for individuals.
Common Examples of Felonies:
- Violent crimes: Murder, assault, armed robbery.
- Property crimes: Burglary, arson.
- Drug offenses: Trafficking, manufacturing, or possession of controlled substances.
- White-collar crimes: Fraud, embezzlement, money laundering.
Felonies are recorded in an individual’s criminal record and are accessible through background checks unless legal actions are taken to remove or conceal them.
How Long Do Felonies Stay on a Background Check?
In general, felonies remain on a background check indefinitely unless specific actions, such as expungement or record sealing, are undertaken. However, the time a felony appears on a background check can vary depending on several factors:
- State Laws:
- Some states enforce a seven-year rule limiting the reporting of criminal records after seven years. For instance:
- California, Texas, and New York restrict reporting of criminal records after seven years unless the salary exceeds a certain threshold.
- Other states, like Florida and Indiana, allow felonies to remain on record indefinitely.
- Some states enforce a seven-year rule limiting the reporting of criminal records after seven years. For instance:
- Type of Background Check:
- Basic checks: May only show recent criminal history (e.g., last 7–10 years).
- Comprehensive checks: Often reveal a lifetime of criminal history, including older felonies.
- Nature of the Crime: Felonies involving violence, sexual offenses, or major fraud are more likely to appear due to their seriousness.
- Employer or Agency Requirements: Organizations in certain industries (e.g., finance, healthcare, childcare) may mandate stricter and more detailed background checks that include older felonies.
Will a 20-Year-Old Felony Show Up?
Whether a 20-year-old felony appears on a background check depends on several factors:
- State-Specific Reporting Rules: States with reporting limits may exclude felonies older than seven or ten years. For instance:
- Texas: Felonies older than seven years may not show up unless salary thresholds are met.
- New York: Similar restrictions apply for certain positions.
- Expungement or Sealed Records: If the felony has been expunged or sealed, it will not appear on standard background checks. However, certain entities (e.g., law enforcement or government agencies) may still access sealed records.
- Type of Screening: Comprehensive or federal background checks may include older felonies, whereas basic employment screenings may focus only on recent history.
For individuals concerned about their records, understanding state laws and the nature of the screening process is critical.
What Determines What Appears on a Background Check?
The results of a background check are influenced by several factors, including legal regulations, the type of screening conducted, and the policies of the organization requesting the check. Below are key factors that determine whether a 20-year-old felony may appear:
1. State Laws
State regulations significantly impact what information can be included in a background check.
- Seven-Year Rule: Many states, such as California, New York, and Texas, limit the reporting of criminal records to the past seven years for jobs paying below a certain salary threshold.
- Indefinite Reporting: States like Florida, Indiana, and Wisconsin allow felonies to remain on records indefinitely unless expunged or sealed.
2. Type of Background Check
The scope of the background check directly influences the results:
- Basic Employment Checks: Often focus on the past 7–10 years of criminal history.
- Comprehensive Criminal Checks: Can include lifetime records, revealing older felonies.
- Federal Background Checks: Typically reveal federal offenses and serious crimes, regardless of how old they are.
3. Employer Policies and Industry Standards
Employers have varying policies regarding criminal records based on industry requirements and job responsibilities:
- Sensitive Positions: Jobs in finance, healthcare, education, or law enforcement often require in-depth screenings that include older records.
- General Positions: Retail or entry-level jobs may focus only on recent convictions.
4. The Nature of the Felony
The type and severity of the felony can also affect its visibility:
- Violent and Sexual Crimes: These offenses are more likely to appear on background checks due to their seriousness.
- Nonviolent Offenses: Felonies like minor theft or possession may not be prioritized in basic screenings, especially after decades.
When a 20-Year-Old Felony May or May Not Appear
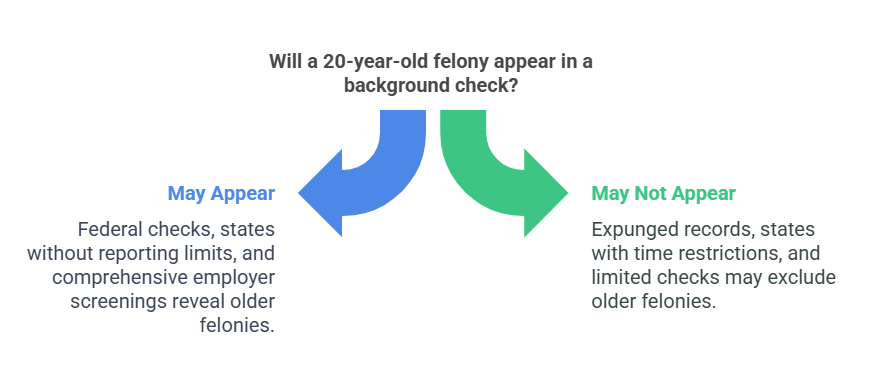
Scenarios Where It May Appear:
- Federal Background Checks: Conducted for high-security positions, these checks reveal all felonies, regardless of age.
- State Without Reporting Limits: In states like Florida, felonies remain on records indefinitely unless legally removed.
- Comprehensive Employer Screenings: Organizations in sensitive industries often conduct detailed checks that include older crimes.
Scenarios Where It May Not Appear:
- Expunged or Sealed Records: Felonies removed or hidden through legal processes are inaccessible to most employers.
- States With Time Restrictions: Felonies older than seven years may not be reported in states like California or Texas for certain jobs.
- Limited Background Checks: Standard employment checks focusing on recent history may exclude older records.
The Role of Expungement and Record Sealing
Expungement and record sealing are crucial legal processes that can remove or restrict access to criminal records, including felonies.
What Is Expungement?
Expungement permanently removes a criminal record from public access. Once a felony is expunged, it will not appear on standard background checks. Eligibility varies by state and crime.
Steps to Expunge a Felony Record:
- Check Eligibility: Confirm that the felony qualifies for expungement under state law.
- File a Petition: Submit a request to the court where the conviction occurred.
- Attend a Hearing: Present your case if required by the court.
- Receive the Expungement Order: Once granted, the record is removed from public databases.
What Is Record Sealing?
Sealing a record restricts public access but does not erase the record entirely. Sealed records may still be accessible to law enforcement, courts, and certain employers.
Key Differences Between Expungement and Sealing:
- Expungement: Completely erases the record from public access.
- Sealing: Hides the record from most entities but retains it for specific purposes.
ExactBackgroundChecks: Accurate and Reliable Solutions
For individuals and organizations seeking thorough background check services, ExactBackgroundChecks offers a range of solutions tailored to meet various needs.
Services Provided by ExactBackgroundChecks:
- Criminal History Reports: Detailed reviews of felony and misdemeanor records.
- Employment Screening: Verification of employment history, education, and references.
- Compliance Assistance: Ensures adherence to FCRA, EEOC, and state laws.
Why Choose ExactBackgroundChecks?
- Comprehensive Results: Access to nationwide and state-specific databases.
- Customizable Packages: Tailored solutions for industries like healthcare, finance, and education.
- Expert Support: Guidance for complex cases, including expunged or sealed records.
ExactBackgroundChecks helps both individuals and employers make informed decisions by delivering accurate and up-to-date information.
Comparison of Background Check Types
| Type of Background Check | What It Covers | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Criminal Background Check | Felonies, misdemeanors, arrests | Employment, housing, licensing |
| Federal Background Check | Federal crimes (e.g., fraud, terrorism) | Government jobs, high-security roles |
| Civil Background Check | Lawsuits, judgments, liens | Tenant screening, business partnerships |
| Credit Background Check | Credit score, financial history | Financial jobs, loans |
| Employment Verification | Job titles, employers, references | Hiring decisions, career screenings |
Legal Aspects Surrounding Background Checks
When it comes to background checks and the appearance of a 20-year-old felony, several legal frameworks govern how information is accessed and used. These regulations aim to balance employer needs and the rights of individuals seeking employment. Here are some key legal aspects to consider:
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA):
The FCRA regulates how consumer reporting agencies handle background check data. Employers must notify candidates before conducting a background check and obtain written consent. If adverse action is taken due to a background check (e.g., denying a job), the employer must provide a copy of the report and inform the individual of their rights. - State-Specific Laws:
Many states have laws limiting how far back background checks can go. For example, in states like California and Texas, most criminal convictions older than seven years may not appear on standard checks, except for specific roles such as those in finance or law enforcement. - Ban the Box Legislation:
“Ban the Box” laws prohibit employers from asking about criminal history on initial job applications. These laws aim to give individuals with past convictions a fair chance to compete for jobs based on qualifications rather than criminal records. - Expungement and Sealing Laws:
Expunged or sealed records are typically removed from public access and background checks. However, certain employers (e.g., federal agencies or positions requiring security clearance) may still access this information. - Industry-Specific Regulations:
Some industries, such as healthcare, education, and childcare, have stricter rules regarding background checks. Felonies may remain visible regardless of age due to the sensitive nature of these roles.
FAQs About Background Checks and Employment Screening
Here are five frequently asked questions regarding background checks and employment screening, along with detailed answers:
Do felonies ever disappear from background checks?
Felonies can remain on background checks indefinitely unless they are expunged or sealed. However, many states impose a "lookback" period, often seven or ten years, after which non-violent or older convictions may no longer appear.
Can an employer deny me a job for a felony from 20 years ago?
Yes, an employer can deny employment based on a felony if it is relevant to the role or company policy. However, under FCRA and some state laws, employers must ensure the conviction is relevant to job responsibilities and give the candidate an opportunity to explain.
How do state laws affect background check results?
State laws vary widely. In some states, criminal records older than seven years are not reported on standard checks, while others allow full disclosure. Additionally, states with Ban the Box laws delay inquiries about criminal history until later in the hiring process.
What’s the difference between an expunged and sealed record?
- Expunged Record: Legally treated as if it never happened. The record is erased and no longer appears in background checks.
- Sealed Record: Hidden from public view but may still be accessed by specific entities, such as law enforcement or federal employers.
What information does a basic employment background check include?
A basic employment background check typically includes:
- Criminal history (if applicable under state laws)
- Employment verification
- Education verification
- Identity verification
- Credit history (if relevant to the role)
Conclusion
Understanding how a 20-year-old felony might impact a background check involves knowing the legal, procedural, and contextual factors at play. While many felonies may appear indefinitely, factors such as state laws, the nature of the job, and record expungement can significantly influence the outcome.
Employers must navigate background checks carefully, adhering to legal requirements like the FCRA and Ban the Box laws. At the same time, job seekers with older convictions should explore options like record sealing or expungement to improve their chances of employment.
For accurate and reliable background check services, exactbackgroundchecks is here to assist. We provide a wide range of solutions, including criminal history reports, employment screening, and compliance guidance, ensuring employers make informed hiring decisions while staying compliant with the law.