Quick Background Check: A How-To for Beginners

Understanding Quick Background Checks
In today’s fast-paced world, the need for speed and efficiency permeates every aspect of our personal and professional lives, and background checks are no exception. Whether you are hiring a new employee, screening a potential tenant, or verifying a new business partner, a quick background check can provide vital information in a fraction of the time that traditional background checks would require. This article will explore what a quick background check is, how it differs from comprehensive checks, the various types of checks available, and why individuals and businesses opt for faster screening solutions. We will also look at some real-world scenarios where quick background checks are essential, providing you with an in-depth understanding of this growing trend.
What is a Quick Background Check?
A quick background check is essentially a streamlined version of a comprehensive background check, focusing on gathering key information in a short period of time. Unlike full background checks, which may take days or even weeks to process due to their thorough nature, quick background checks are designed to deliver important data fast—often within hours or a couple of days. These checks tend to cover only the most essential and relevant aspects of an individual’s history, allowing employers, landlords, and businesses to make informed decisions without delays.
While traditional background checks may investigate criminal history, employment history, educational qualifications, credit history, and more, a quick background check narrows the scope, often focusing on criminal records, identity verification, and employment verification. The goal is to provide a fast snapshot of a person’s history to assist in time-sensitive decisions, particularly when a decision needs to be made quickly.
Key Differences Between Quick Background Checks and Comprehensive Background Checks
The most obvious difference between a quick background check and a comprehensive one is the depth of the investigation. Comprehensive background checks tend to be more thorough and involve multiple sources of information. These checks may include:
- Criminal records (local, state, and federal): A comprehensive criminal history check will delve deeper into an individual’s background, including minor offenses or infractions, as well as more serious convictions that may not immediately show up on a quick check.
- Credit reports: Comprehensive checks will provide a detailed analysis of an individual’s financial history, including credit score, bankruptcies, liens, and any outstanding debts.
- Employment and educational history: These checks thoroughly verify the accuracy of an individual’s job and academic credentials, cross-referencing multiple sources.
- References and additional screening: A detailed check may even involve contacting personal or professional references to verify additional aspects of an individual’s history.
In contrast, a quick background check typically focuses on gathering only the essential details needed for immediate decision-making. This often includes:
- Criminal record checks: Only relevant offenses (e.g., felonies, sex offenses, or serious misdemeanors) may be screened.
- Employment verification: This may include confirming job titles, employment dates, and any major gaps in employment.
- Identity verification: This ensures that the person you’re screening is who they say they are, confirming details such as date of birth, social security number, and address.
Because of its narrower scope, a quick background check can be completed much faster than a comprehensive check, often in a matter of hours or days. However, it is important to note that while quick background checks are incredibly useful, they do not provide the same depth of information as a more extensive screening.
Types of Quick Background Checks
Various types of background checks can be performed quickly, each serving a different purpose depending on the situation. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Criminal Record Checks
One of the most popular reasons for conducting a background check is to verify whether an individual has a criminal history. Criminal record checks may include:
- Felonies and Misdemeanors: A quick criminal background check typically identifies felony convictions and major misdemeanors. Depending on the jurisdiction, minor offenses may not appear.
- Sex Offender Registry: For certain roles, employers and landlords may need to verify whether the individual has any offenses related to sexual crimes. Quick checks can cross-reference state or national sex offender databases to ensure the person has no such offenses in their history.
- Warrants: Some checks also reveal whether a person has any active arrest warrants.
These checks are typically completed within a few hours to a day, depending on the jurisdiction and the database being searched.
2. Employment Verification
Employment verification checks are commonly conducted by employers to ensure that job candidates have accurately represented their past employment. These checks can confirm:
- Job titles and positions held: The check verifies that the applicant has the qualifications they claim.
- Employment dates: This can help uncover any discrepancies in the candidate’s resume or job application.
- Salary information: In some cases, employers may also verify salary details, although this is less common and typically occurs only for higher-level positions.
A quick employment verification check is typically completed within a business day or two, depending on the responsiveness of the previous employer or the verification service used.
3. Credit Reports
Although a comprehensive credit report can be extensive, a quick background check may offer a snapshot of an individual’s credit status. This typically includes:
- Credit score: The applicant’s creditworthiness is evaluated based on their credit score.
- Outstanding debts and liabilities: This may include any unpaid loans, mortgages, or credit card balances.
- Bankruptcies and financial judgments: If the person has declared bankruptcy or is involved in any legal financial disputes, these issues may be flagged during a quick credit check.
Quick credit reports can often be accessed in minutes, making them an excellent choice for employers who want to verify the financial responsibility of a potential hire.
4. Identity Verification
Identity verification ensures that the person you’re screening is who they say they are. This can include:
- Social Security Number (SSN) check: A quick identity check can validate an individual’s SSN, ensuring it matches their name and other details.
- Address and contact details: The service may also cross-reference an individual’s stated address and phone number with public records to confirm they are legitimate.
- Date of birth check: Ensuring the date of birth matches the records can prevent fraudulent applicants from applying.
This type of check is typically completed within minutes to hours, especially when performed by professional online verification services.
Why Choose a Quick Background Check?
A quick background check is an attractive option for both individuals and businesses looking to make quick, informed decisions. The reasons for opting for a quick check are varied and can be driven by several factors, including:
1. Time Sensitivity
In industries where hiring decisions need to be made quickly, such as retail, hospitality, or temporary staffing, a fast background check is essential. Employers may need to hire someone urgently due to high turnover, seasonal demands, or other factors. By opting for a quick background check, they can assess the basic qualifications of candidates without delay.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
A comprehensive background check can be expensive, particularly when it involves multiple types of checks. For businesses with many applicants, or for individuals needing to conduct multiple screenings, a quick background check provides a more affordable option. Quick checks typically cost less than detailed screenings because they cover only the essential information, saving time and money.
3. Ease of Use
Quick background checks are often easier to complete than comprehensive checks. Many services are available online, allowing individuals and businesses to perform background checks with minimal effort. After submitting basic information, results are often provided within a few hours to a day, and the process can be managed entirely through online platforms. This convenience makes quick checks a preferred option for those with little time or experience in background screening.
Scenarios Where Quick Background Checks Are Necessary
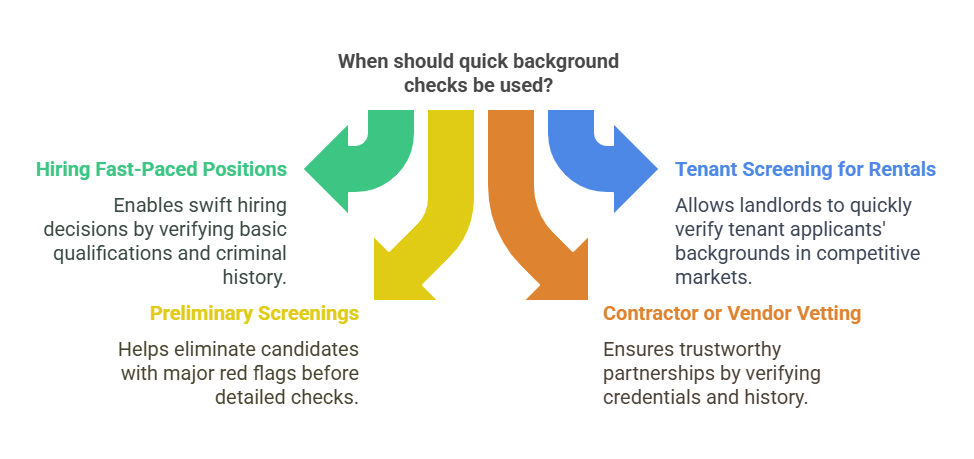
Quick background checks are increasingly being used in a variety of situations where speed is essential. Some of these scenarios include:
1. Hiring Fast-Paced Positions
In industries with high employee turnover or those requiring fast onboarding, such as retail or hospitality, employers may need to make swift hiring decisions. A quick background check enables employers to verify basic qualifications and criminal history before offering a position.
2. Tenant Screening for Rentals
Landlords often require quick background checks when selecting tenants for rental properties. They need to verify an applicant’s criminal record, employment history, and identity as part of the screening process. Given the competitive nature of rental markets, tenants frequently seek to apply to multiple properties, and landlords want to expedite the screening process without sacrificing due diligence.
3. Preliminary Screenings Before Full Background Checks
Sometimes, employers and businesses conduct a quick background check as an initial screening before moving on to a more comprehensive investigation. This is especially helpful when dealing with a large pool of applicants, allowing the employer to quickly eliminate any candidates with major red flags before investing in a more detailed check.
4. Contractor or Vendor Vetting
Businesses that rely on third-party contractors, vendors, or consultants may use quick background checks to verify the credentials and criminal history of potential partners. This ensures that they are working with trustworthy individuals and companies without delays or unnecessary hurdles.
Increasing Demand for Quick Background Checks
The growing demand for quick background checks reflects changes in industries that rely on fast hiring and tenant screening processes. According to recent reports, more than 90% of employers in the U.S. conduct background checks on potential employees. Of these employers, a significant portion is increasingly utilizing quick checks to streamline the screening process, particularly in the retail, healthcare, and gig economy sectors.
As the need for speed continues to rise in recruitment and other industries, quick background checks are becoming an integral part of modern hiring and screening practices.
How to Perform a Quick Background Check
In today’s fast-moving world, the ability to perform a quick background check is not just a luxury; it is a necessity for individuals and businesses that need to make informed decisions swiftly. Whether you’re a business owner hiring a new employee, a landlord screening a tenant, or a company vetting a contractor, knowing how to conduct a quick background check can save you valuable time. This section will walk you through the steps involved in performing a quick background check, the benefits of using professional services, and the various platforms available for conducting fast and reliable checks.
Steps to Perform a Quick Background Check
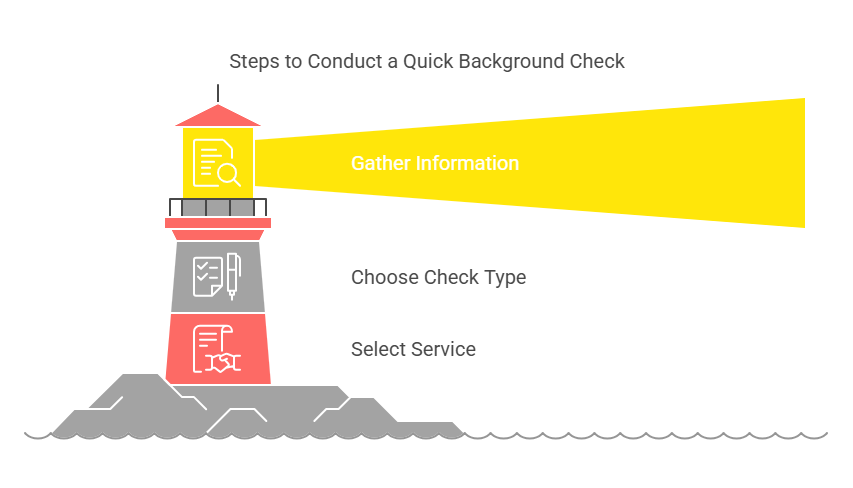
Performing a quick background check is a straightforward process, but there are key steps to follow to ensure accuracy and compliance with legal requirements. Below are the essential steps involved:
1. Gather Basic Information
Before initiating a background check, it is critical to collect the necessary personal details of the individual being screened. These may include:
- Full name: Ensure that the name matches the person’s official documents, such as a driver’s license or social security card.
- Date of birth: The date of birth is crucial for verifying the individual’s identity and differentiating between people with similar names.
- Social Security Number (SSN): This number allows for a more detailed and accurate check, particularly for criminal records and credit reports.
- Address history: A person’s past addresses can be important when checking criminal records or verifying identity.
- Other identifiers: Additional information, such as phone numbers or email addresses, can help verify the person’s identity.
Having this information at hand will make the process faster and more efficient, ensuring that the background check is conducted on the correct individual.
2. Choose the Type of Background Check
The next step is to determine the type of background check that is needed. Depending on the purpose of the check (e.g., hiring, tenant screening, etc.), you may only need to perform one or two specific checks. Common types of quick background checks include:
- Criminal Record Check: This is one of the most common checks, verifying whether the individual has any criminal history, including felony convictions, sex offenses, or misdemeanors.
- Employment Verification: Confirming the individual’s work history is crucial for ensuring the accuracy of resumes or applications, as well as understanding job responsibilities and employment gaps.
- Identity Verification: This helps verify that the individual is who they claim to be, using information such as their SSN, date of birth, and address history.
- Credit Check: For positions that require financial responsibility, such as in banking or finance, a quick credit report can provide an overview of the individual’s financial stability.
By focusing on one or two aspects of an individual’s history, a quick background check can be completed in a fraction of the time it takes to conduct a more comprehensive check.
3. Select a Background Check Service
Once the information is gathered and the type of background check is chosen, the next step is to decide how to obtain the check. There are several ways to access background check services, each with different levels of convenience, cost, and speed.
Using Online Background Check Platforms
One of the fastest and most popular methods for obtaining a quick background check is to use an online background check platform. These services have made the process incredibly easy for both individuals and businesses. Many of them provide quick, real-time results, offering you the ability to perform a background check in as little as a few minutes to a few hours. Here are some key details to consider when selecting an online platform:
1. Professional Background Check Services (e.g., Exact Background Checks)
For businesses or individuals who need quick yet reliable results, professional background check services such as Exact Background Checks offer a comprehensive solution. These services streamline the background check process, reducing the hassle of searching for information manually. Some benefits of using services like Exact Background Checks include:
- Quick Turnaround Time: These services provide fast and accurate results, typically within hours or a day.
- Compliance with Legal Standards: Professional services ensure that background checks are conducted in compliance with laws like the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), preventing legal issues that could arise from mishandling sensitive information.
- Accurate Results: Using a professional service guarantees that the information provided is correct and up-to-date, reducing the chances of errors or misinformation.
By using Exact Background Checks, employers and individuals can save time and avoid the complexities of manual background checking, making it easier to verify the information needed to make informed decisions.
2. Online Platforms for DIY Checks
If you’re an individual or small business and prefer to perform background checks on your own, there are several DIY platforms that allow you to quickly search public records databases for criminal history, employment history, and more. Some popular online services include:
- Instant Checkmate
- BeenVerified
- TruthFinder
These services typically offer background checks for a fee, and the results can be accessed online within minutes to a few hours. However, keep in mind that the accuracy of these platforms can vary. Some may not have access to all available records or may rely on outdated information, so it’s important to choose a reputable provider.
3. Government Websites and Public Records
In some cases, you may be able to conduct a quick background check by accessing public records or government websites directly. For example, many states offer online databases for criminal records or sex offender registries. While this option is free, it is often more time-consuming and may not provide as comprehensive a report as a professional service. Additionally, some records may not be accessible online, requiring in-person requests or written applications, which could further delay the process.
4. Third-Party Verification Services
Another option for performing quick background checks is to use third-party verification services. These companies specialize in verifying employment, education, and other credentials quickly. Examples of such services include:
- The Work Number: This service provides employment verification for individuals who have worked at participating companies.
- TransUnion and Equifax: These credit bureaus offer credit checks that can be accessed quickly for financial background checks.
These third-party services can be useful when you need specific types of verification (e.g., employment history, credit report) and want fast results.
Comparing the Options: Pros and Cons
When deciding which method to use for a quick background check, it’s important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option. Below is a comparison table to help you make an informed choice:
| Option | Pros | Cons | Typical Processing Time | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Professional Services (Exact Background Checks) | Fast, reliable, legally compliant | Can be more expensive than DIY options | Hours to 1-2 business days | Moderate to High |
| DIY Platforms (e.g., Instant Checkmate) | Quick access, inexpensive | May provide less accurate or incomplete info | Minutes to a few hours | Low to Moderate |
| Government Websites/Public Records | Free, reliable data | Can be time-consuming, incomplete | Varies, can take days | Free |
| Third-Party Verification Services | Quick, specific verifications (e.g., credit, employment) | Limited scope, may not cover criminal records | Minutes to a few hours | Low to Moderate |
What You Need to Know About Legal Considerations
While quick background checks are convenient, it is important to keep legal considerations in mind. In many cases, performing a background check requires consent from the individual being screened. This is especially true if you are obtaining credit reports or criminal records.
Before conducting any background check, ensure that you have obtained written consent from the person whose background you are checking, as failure to do so can lead to legal issues. Additionally, background checks must comply with laws like the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) in the U.S., which protects individuals’ privacy and ensures that background checks are conducted fairly.
Moreover, certain states and local jurisdictions have their own laws that regulate how and when background checks can be conducted. For example, some states have “ban-the-box” laws that prevent employers from asking about criminal history until after a job offer is made. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the legal requirements in your area or industry to ensure that your background checks are compliant.
Legal Aspects of Quick Background Checks
Understanding the legal framework surrounding quick background checks is essential for employers, individuals, and organizations alike. Here are the critical legal aspects to consider:
1. Consent Requirements
In most cases, conducting a background check without the consent of the individual being screened is illegal. Consent is required for obtaining information related to criminal history, employment, credit, or personal records. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) mandates that the individual must be informed that a background check will be conducted and provide written consent.
For example, in the hiring process, employers typically ask applicants to sign a consent form that grants permission to perform a background check. If the employer fails to obtain consent, they could face legal repercussions and the inability to use the results of the background check in their decision-making process.
2. FCRA Compliance
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs the use of consumer information, including background check data. Under the FCRA, employers must adhere to specific guidelines when conducting background checks, including:
- Disclosure: Employers must disclose to the individual that they will be conducting a background check.
- Notification: If an employer decides not to hire someone based on the results of a background check, they must provide the applicant with a copy of the report and a notice of their rights under the FCRA.
- Accuracy: The information gathered in a background check must be accurate and up-to-date. If the individual disputes the results of the check, they have the right to challenge and request a correction.
FCRA compliance is crucial to avoid any legal pitfalls when using the results of a quick background check in decision-making processes.
3. State-Specific Laws
In addition to the FCRA, states and local jurisdictions may have their own laws that regulate background checks. Some common state-specific laws include:
- Ban-the-Box Laws: These laws prohibit employers from asking about criminal history on initial job applications. Instead, employers must wait until later in the hiring process (usually after an interview or job offer) to inquire about criminal records. These laws are designed to reduce barriers to employment for individuals with past convictions.
- Expungement and Sealing of Records: In some states, individuals who have been convicted of a crime may be able to have their records sealed or expunged, making it difficult or impossible to obtain certain criminal records during a background check.
- Drug Testing Laws: Some states have laws regarding when and how employers can conduct drug tests. For instance, certain states require employers to have a specific policy in place or mandate that drug tests are conducted only under certain circumstances.
Employers and individuals should familiarize themselves with local laws to ensure their background checks comply with all applicable regulations.
4. Privacy Laws and Protection of Personal Information
Background checks often involve the collection of sensitive personal information, such as Social Security numbers, credit histories, and criminal records. As a result, privacy protection is a critical concern. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), for example, governs the processing of personal data for residents of the European Union (EU), ensuring that the individual’s privacy is respected during the background check process.
Employers and individuals conducting background checks must be mindful of how personal data is handled, stored, and shared. Unauthorized access to or sharing of this information can lead to data breaches and potential legal actions.
5. Legal Risks for Employers
If an employer mishandles a quick background check, they may face several legal risks, including:
- Discrimination: If an employer uses background check results to discriminate against a protected class (e.g., race, gender, disability), they may be violating anti-discrimination laws. For example, a criminal history should not be used as a blanket reason to disqualify candidates unless it is directly related to the job.
- Negligent Hiring: Employers are legally obligated to conduct thorough background checks for roles that involve safety-sensitive tasks (e.g., handling hazardous materials, working with vulnerable populations). Failure to do so may expose employers to lawsuits if an employee’s past behavior leads to harm.
- Inaccurate Information: If an employer uses inaccurate or outdated information from a background check to make hiring decisions, the individual may have grounds for legal action.
Ensuring proper legal procedures are followed will protect employers from these risks and ensure fair treatment for all applicants.
FAQs About Quick Background Checks
Here are some frequently asked questions about quick background checks, along with detailed answers to provide clarity on common concerns:
What is the primary difference between a quick background check and a comprehensive background check?
A quick background check focuses on essential information like criminal records, employment verification, and identity verification, delivering results rapidly. A comprehensive check delves deeper into areas like credit reports, detailed educational history, and references, taking more time.
Why might a business choose a quick background check over a comprehensive one?
Businesses may choose quick background checks for time-sensitive hiring, cost-effectiveness, ease of use, or as a preliminary screening tool before conducting a more detailed investigation.
What types of information are typically included in a quick criminal record check?
A quick criminal record check typically includes felonies, major misdemeanors, sex offender registry status, and active arrest warrants.
What are the key steps involved in performing a quick background check?
The key steps are gathering basic information, choosing the type of background check needed, selecting a background check service (online platform, government resource, etc.), and ensuring legal compliance.
What legal considerations are essential when conducting a quick background check?
Essential legal considerations include obtaining consent, complying with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), adhering to state-specific laws (like "ban-the-box" laws), protecting personal data privacy, and avoiding discrimination or negligent hiring.
What is the primary difference between a quick background check and a comprehensive background check?
A quick background check focuses on essential information like criminal records, employment verification, and identity verification, delivering results rapidly. A comprehensive check delves deeper into areas like credit reports, detailed educational history, and references, taking more time.
Why might a business choose a quick background check over a comprehensive one?
Businesses may choose quick background checks for time-sensitive hiring, cost-effectiveness, ease of use, or as a preliminary screening tool before conducting a more detailed investigation.
What types of information are typically included in a quick criminal record check?
A quick criminal record check typically includes felonies, major misdemeanors, sex offender registry status, and active arrest warrants.
What are the key steps involved in performing a quick background check?
The key steps are gathering basic information, choosing the type of background check needed, selecting a background check service (online platform, government resource, etc.), and ensuring legal compliance.
What legal considerations are essential when conducting a quick background check?
Essential legal considerations include obtaining consent, complying with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), adhering to state-specific laws (like "ban-the-box" laws), protecting personal data privacy, and avoiding discrimination or negligent hiring.
Conclusion
Quick background checks are an invaluable tool for individuals and businesses looking to make fast, informed decisions. Whether you’re hiring a new employee, screening a tenant, or verifying a contractor’s credentials, knowing how to conduct a quick and legally compliant background check can help mitigate risks and ensure that your decisions are well-informed.
In this article, we’ve covered how to perform a quick background check, the legal aspects involved, and the most common FAQs regarding the process. Understanding the importance of consent, FCRA compliance, and the potential legal risks is essential for anyone conducting background checks. Remember, using a professional service like Exact Background Checks can help you obtain accurate, fast, and legally compliant results with minimal hassle.



Quick background checks are a game-changer for businesses and individuals needing fast, reliable information for hiring, tenant screening, or contractor vetting. While they don’t offer the depth of comprehensive checks, they provide essential details like criminal records, employment history, and identity verification in a fraction of the time. Always ensure compliance with legal requirements like the FCRA and obtain proper consent to avoid legal pitfalls. Staying informed and using reputable services can make the process smooth and efficient.