Key Facts About Employment History in Background Checks

Understanding Background Checks and Employment History
A background check is a process employers use to investigate the history of job applicants to verify their qualifications, assess their integrity, and identify any potential red flags that could affect their suitability for a job. These checks are an essential part of the hiring process and are designed to ensure that candidates are honest about their background and possess the skills and experience required for the position.
Background checks can vary depending on the nature of the job and the employer’s requirements. Some checks may be simple, involving basic identity verification, while others can be thorough and detailed, delving into criminal records, credit history, and employment background. Employers use background checks to reduce risk, improve workplace safety, and ensure that they are hiring individuals who align with the company’s values and requirements.
Why Employers Use Background Checks
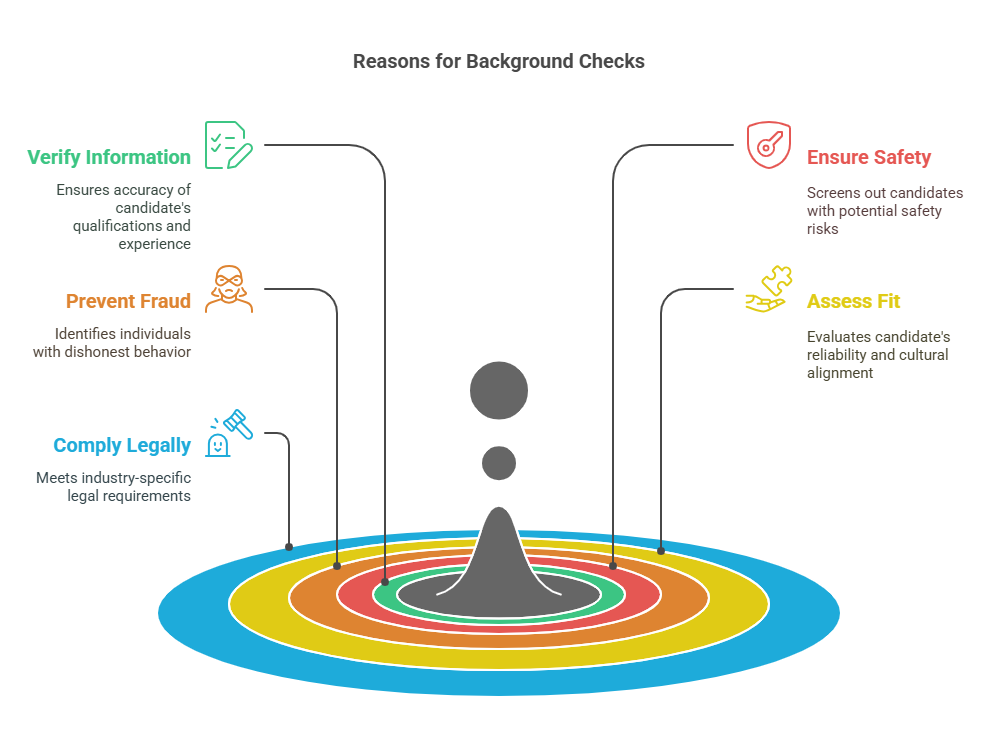
Employers perform background checks for several key reasons, including:
- Verify Candidate Information: Background checks allow employers to confirm the information provided by candidates on their resumes or job applications. This ensures that the candidate is not misrepresenting their qualifications or work experience.
- Ensure Workplace Safety: Employers want to create a safe and secure work environment for all employees. By conducting background checks, they can screen out candidates with criminal histories or other red flags that may pose a safety risk to others.
- Prevent Fraud and Theft: Background checks can help employers identify individuals with a history of fraud, theft, or other dishonest behavior. This is particularly important for positions that involve handling finances, sensitive information, or access to company assets.
- Assess Cultural Fit and Reliability: Background checks can give employers a better understanding of a candidate’s reliability, work ethic, and overall behavior in the workplace. This information helps employers gauge whether a candidate will fit into the company’s culture and values.
- Comply with Legal Requirements: Certain industries, such as healthcare, finance, and education, may have legal or regulatory requirements for conducting background checks on employees. These checks help employers remain compliant with laws governing employee safety and integrity.
Types of Background Checks
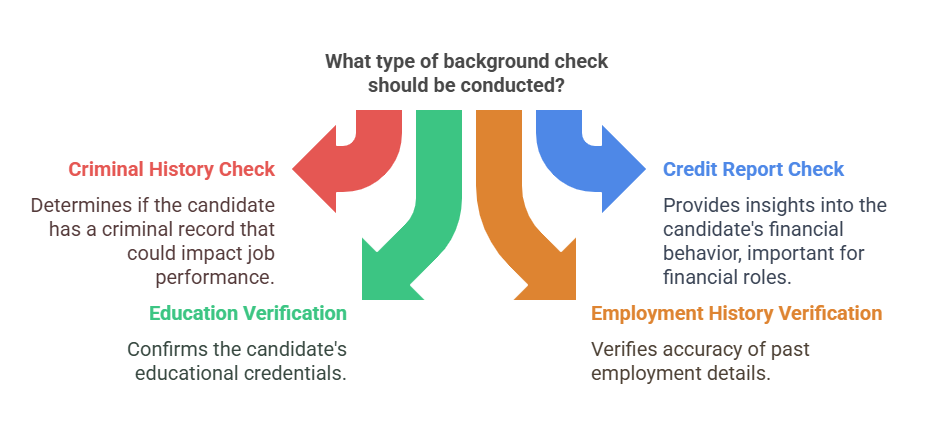
Background checks can uncover a wide range of information about a job candidate, depending on the specific type of check conducted. The most common types of background checks include:
- Criminal History Check: This is one of the most common types of background checks. Employers use criminal history checks to determine if an applicant has a criminal record, including misdemeanors, felonies, or other legal issues that might affect their ability to perform a job.
- Credit Report Check: Employers may check a candidate’s credit history, particularly for positions that involve financial responsibilities. This check provides insights into the candidate’s financial behavior and whether they have any history of bankruptcy, debt, or other financial issues.
- Education Verification: Employers often verify the educational credentials listed by the candidate, ensuring that they hold the degrees or certifications claimed.
- Employment History Verification: This type of check verifies the accuracy of a candidate’s employment history. It includes confirming job titles, dates of employment, and reasons for leaving past positions.
- Reference Check: Employers may contact references provided by the candidate to gather additional information about their qualifications, work ethic, and character.
- Drug Testing: Some employers may require candidates to undergo drug testing as part of the background check process to ensure that the candidate is fit for the role.
- Driving Record Check: For positions that involve driving, employers may check the candidate’s driving record to assess their safety and reliability on the road.
- Social Media and Online Presence Check: Some employers may check a candidate’s social media profiles or online presence to gain further insights into their personality and behavior.
Does a Background Check Show Employment History?
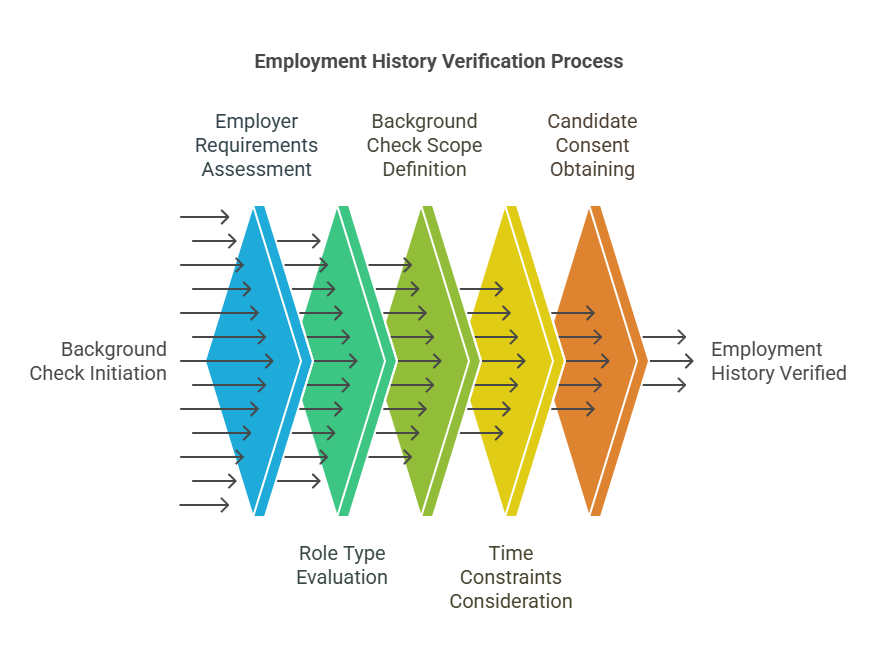
Employment history verification is an essential part of the background check process, but it is not automatically included in every background check. Whether or not employment history is included in a background check depends on the employer’s requirements, the position being applied for, and the nature of the background check being conducted.
In many cases, employment history verification is a standard component of a background check, especially for positions where prior experience is critical to the job. For example, roles in industries such as healthcare, finance, or law may require a thorough review of a candidate’s previous employment to ensure they have the relevant experience and qualifications.
However, there are some factors that influence whether or not employment history is included in a background check:
- Employer Requirements: Employers often have their own criteria for conducting background checks. Some employers may prioritize criminal checks or credit reports over employment history verification, particularly for entry-level positions where prior work experience is less critical.
- Type of Role: For high-level positions or roles that require significant expertise or specialized knowledge, verifying employment history may be more important. In contrast, for jobs that do not require specific prior experience, employment history may not be thoroughly checked.
- Scope of the Background Check: The extent of a background check varies by employer. Some background checks are basic and only include criminal history checks, while others are comprehensive and may include employment history verification.
- Time Constraints: In some cases, time constraints or urgency in filling a position may result in a background check that focuses more on criminal history or credit checks rather than thoroughly verifying employment history. While employment history verification may not take as long as criminal checks, it may still involve contacting previous employers or using third-party services to confirm details.
- Candidate’s Consent: For employment history to be verified, the candidate must provide consent. Employers must obtain written consent from the candidate before contacting previous employers for verification purposes. If the candidate does not provide consent, employers may be limited in verifying employment history.
How Employment History is Verified and Factors Affecting It
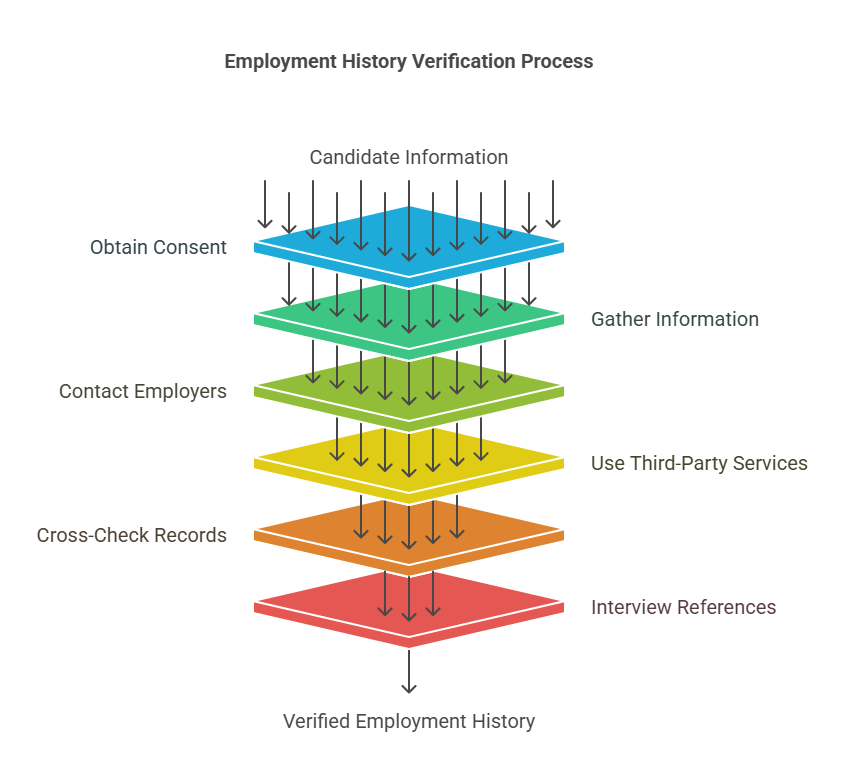
The Process of Verifying Employment History
Verifying employment history is a critical aspect of the background check process that ensures job candidates are truthful about their previous positions, job responsibilities, and employment durations. Employment history verification typically involves several steps, and it is a process that can either be performed by the employer directly or outsourced to a third-party background screening company. Let’s explore the key steps involved in verifying employment history.
- Candidate Consent
Before an employer can begin verifying a candidate’s employment history, they must first obtain written consent from the candidate. Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), employers are required to inform candidates of the background check and obtain permission to proceed. This consent is necessary to protect the candidate’s privacy and ensure that the employer is in compliance with legal regulations. - Gathering Information
Employers generally ask candidates to provide a detailed list of their past employment, including the names of companies they’ve worked for, dates of employment, job titles, and any relevant details regarding their roles. Many employers include this section on job applications, where candidates list their employment history. In some cases, the candidate might also provide a detailed resume or other documentation to support their claims. - Contacting Previous Employers
Once the employer has gathered all the information they need from the candidate, they will proceed to verify the details. The most common method for verifying employment history is to contact the candidate’s previous employers directly. Employers typically contact the human resources (HR) department or other appropriate personnel within the organization to confirm the details provided by the candidate.
The HR representative will confirm:
- Job Title: What role the candidate held within the organization.
- Dates of Employment: The specific start and end dates of the candidate’s employment.
- Reasons for Leaving: Whether the candidate left voluntarily, was terminated, or had another reason for departure.
- Job Responsibilities: A brief description of the candidate’s role and responsibilities in the organization.
- Using Third-Party Verification Services
Employers can outsource the verification of employment history to third-party background check companies, which specialize in handling the verification process. These companies have established relationships with various organizations and can often get in touch with past employers quickly and securely.
Third-party companies such as Exact Background Checks typically have a network of trusted sources to help streamline the employment verification process. By using these services, employers can often obtain faster and more accurate results, and ensure that the verification process is in compliance with all applicable laws.
- Cross-Checking Against Public Records
In some cases, employers may cross-check employment history against public records to verify the candidate’s claims. For example, some states require employers to file specific reports about their employees, which can be accessed for verification purposes. Additionally, tax records may indicate the candidate’s history with specific employers. - Interviews with References
While not always part of the employment verification process, some employers may also choose to contact the candidate’s references or former colleagues to validate the candidate’s experience. These references can provide additional insight into the candidate’s job performance, work ethic, and overall contributions to the company.
What Information is Typically Verified?
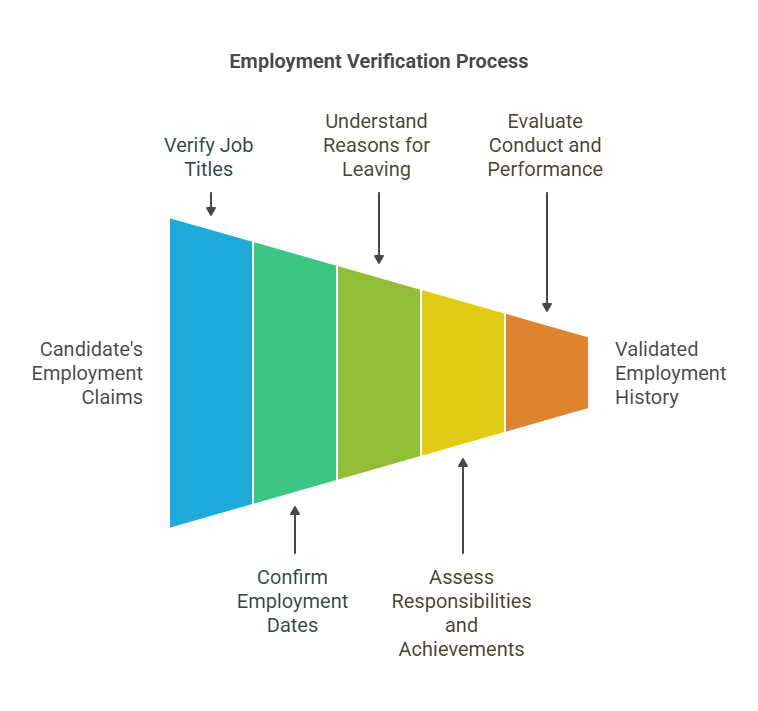
When verifying employment history, the employer typically focuses on a few key pieces of information to ensure that the candidate’s employment claims are legitimate. Here are the main types of information employers will seek to verify:
- Job Titles and Roles
One of the most important aspects of employment verification is confirming that the candidate’s job titles match the roles they listed in their application or resume. Employers will check that the title provided by the candidate matches the official records held by the company. - Employment Dates
Employers will verify the start and end dates of a candidate’s employment. This ensures that the candidate worked for the company for the specified period and helps confirm that there are no gaps in the employment history that might raise concerns. - Reasons for Leaving
Understanding why a candidate left a previous job can provide valuable insights into their behavior and professionalism. Employers often ask HR departments about the candidate’s reasons for leaving—whether it was voluntary, involuntary, or due to external circumstances. Employers may also inquire if the candidate was let go due to performance issues, disciplinary actions, or other concerns. - Job Responsibilities and Achievements
Employers may also inquire about the candidate’s responsibilities at previous jobs, to ensure that the duties align with the claims made by the candidate. In some cases, an employer may also ask for specific achievements, such as sales quotas met, performance evaluations, or any notable contributions to the company. - Conduct and Performance
Some employers may inquire about the candidate’s behavior and work performance while employed with the company. This information can provide insight into the candidate’s reliability, communication skills, and ability to work with others. Employers may want to know whether the candidate was punctual, met deadlines, and followed company policies.
The Role of Third-Party Verification Services
As background checks have become a standard part of the hiring process, many employers have turned to third-party services to handle employment history verification. Third-party background screening companies, such as Exact Background Checks, are often relied upon to streamline the verification process, ensuring accurate results in a timely manner.
Benefits of Using Third-Party Verification Services:
- Faster Processing Times: Third-party services specialize in conducting background checks quickly, meaning employers can receive the results faster than if they were to conduct the checks themselves.
- Access to a Wide Network: Verification services have established relationships with past employers, making it easier to track down hard-to-reach companies or organizations that may not readily provide information.
- Compliance: These companies are well-versed in FCRA regulations and other legal guidelines related to background checks, ensuring compliance throughout the process.
- Increased Accuracy: With the experience and resources of third-party services, employers are more likely to get accurate and reliable employment verification results.
Third-party companies can also offer added security, ensuring that confidential information is handled appropriately, and preventing privacy breaches during the verification process.
Limitations and Discrepancies in Employment History Verification
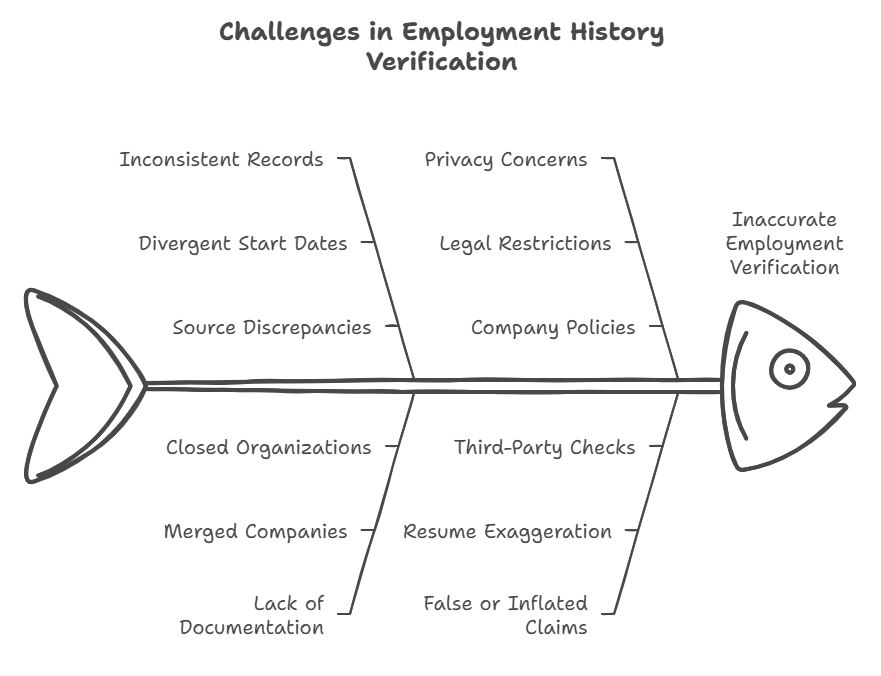
While employment history verification is essential, there are several limitations and factors that can affect the accuracy and reliability of the information provided:
- Inconsistent Records
Sometimes, discrepancies can arise if the candidate’s employment records are incomplete, inaccurate, or inconsistent across different sources. For example, one company may list a candidate’s start date as January 2015, while another source may claim it was in February 2015. These inconsistencies can make it challenging to verify exact dates or details. - Lack of Documentation
In some cases, older companies or organizations may not have well-documented employee records. If a company has been acquired, closed, or merged, it may no longer have easy access to past employee data, which can delay or complicate the verification process. - Privacy Concerns
Some employers may be reluctant to share detailed information about a former employee due to privacy laws or company policies. In such cases, they may provide minimal information, such as job title and dates of employment, but refuse to share reasons for leaving or performance-related details. - False or Inflated Claims
Some candidates may inflate their employment history or provide false information. This can make it difficult for employers to get an accurate picture of a candidate’s work history. Thorough checks, particularly when conducted by third-party verification services, can help uncover such discrepancies. - Timing and Availability
Some candidates may have worked in roles where official documentation is not readily available (such as in freelance or consulting positions). Additionally, candidates who have worked at multiple companies in a short period may present challenges in verifying each job.