How Long Does Employment Verification Take? Key Insights and Timeline

Introduction and Overview of Employment Verification Process
What is Employment Verification?
Employment verification is the process through which an employer or third-party service confirms the details of an individual’s employment history. This verification is typically requested by potential employers, landlords, financial institutions, or government agencies. The purpose of employment verification is to ensure that the information provided by the individual is accurate, such as their job title, dates of employment, salary, and other relevant employment details.
In today’s competitive job market and with increasing concerns over fraud, employment verification has become a crucial step in many hiring, lending, and leasing processes. For employers, it helps verify a candidate’s qualifications and experience, while for landlords and financial institutions, it ensures the person is reliable and can meet financial obligations.
Why is Employment Verification Important?
Employment verification serves several key purposes:
- Confirming Accuracy: Ensures that the job information provided by an applicant is truthful, which can help in preventing resume fraud.
- Assessing Reliability: Verifying a candidate’s previous work experience can give employers an indication of their reliability, work ethic, and performance.
- Ensuring Compliance: In some cases, employment verification is required to comply with laws or regulations (e.g., background checks for financial transactions or certain types of government assistance).
- Risk Mitigation: Verifying an applicant’s job history and income ensures that they are capable of meeting the financial requirements of a job, rental agreement, or loan.
Overview of Employment Verification Process
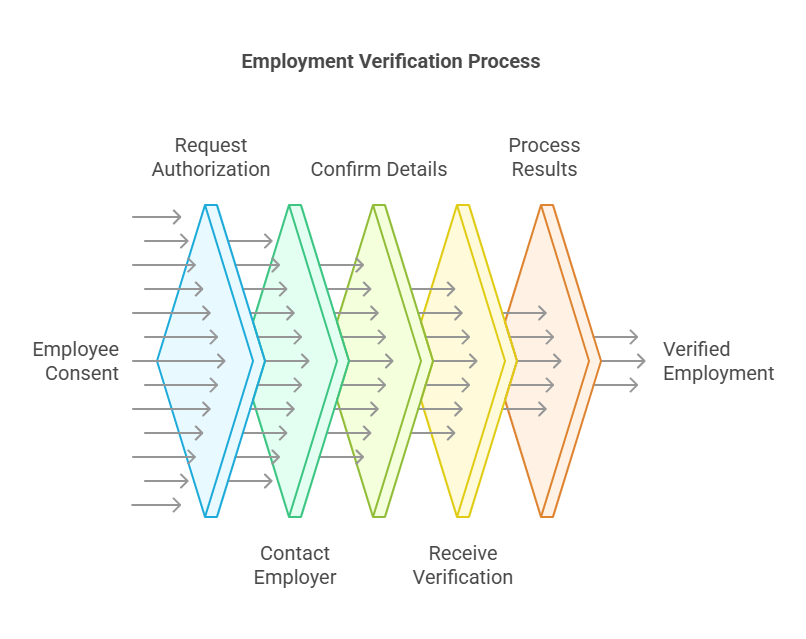
The process of employment verification can vary slightly depending on the entity performing the verification (e.g., employer, landlord, financial institution). However, the general process typically involves the following steps:
- Request for Authorization: The individual (employee or job applicant) is usually asked for their consent to allow an employer or third-party verification company to check their employment details.
- Contacting the Employer: Once authorization is provided, the verifier will contact the employer or former employer to verify employment details. This could be done via phone, email, or through a formal third-party verification service.
- Confirming Employment Details: The primary details that need to be verified include:
- Job title
- Dates of employment
- Salary (if applicable)
- Reason for leaving (if applicable)
- Any other relevant details, such as performance or job responsibilities.
- Receiving the Verification: The employer will respond with the necessary details. Some employers may provide the information directly, while others may require a written request or use third-party services to handle the verification.
- Processing the Results: Once the verification is received, the hiring organization or agency processes the results. If there is any discrepancy or missing information, further follow-up may be required.
How Long Does Employment Verification Take?
The time it takes to complete an employment verification can vary depending on several factors. On average, it may take anywhere from a few hours to several days, but a typical employment verification process generally takes 1 to 3 business days. Below are some factors that influence the timeframe:
Factors Affecting Verification Duration
- Company Size and Structure: Larger organizations or those with centralized HR departments may take longer to process verifications. Smaller companies may have more streamlined procedures but might not have dedicated staff for employment verifications.
- Verification Method Used: The method through which verification is conducted can impact the timeline. Verifying employment via phone or email tends to be quicker than using third-party services, which may require additional processing time.
- Response Time of the Employer: Some employers may take longer to respond due to workload, internal processes, or policies. Larger companies or those with more complex HR structures may also require more time to provide information.
- Availability of Information: If the individual’s employment records are not readily available (e.g., if they worked in a past position that was under a different system), it may take longer for the employer to retrieve and confirm the information.
Verification Methods and Estimated Timeframes
The method used for employment verification can also impact how long it takes to complete the process. Below is a comparison of common verification methods:
| Verification Method | Estimated Timeframe | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Phone Verification | 1-2 Business Days | Fastest method, as it involves directly contacting the employer or HR department. |
| Email Verification | 1-3 Business Days | Involves sending a formal request for information via email. Typically faster than third-party services. |
| Third-Party Services | 3-7 Business Days | Third-party verification services can handle multiple verifications at once, but they may take longer to process. |
| In-Person Verification | 5-10 Business Days | Less common, involves visiting the employer directly. Typically used in very specific or high-security circumstances. |
Factors Affecting the Duration of Employment Verification
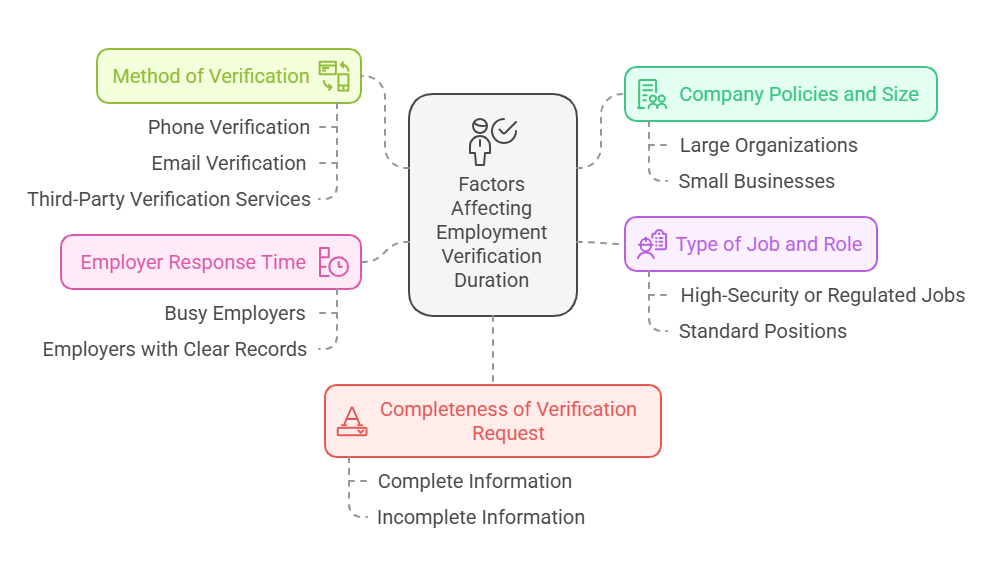
While the average time for employment verification is generally 1 to 3 business days, several factors can either shorten or extend this timeline. Understanding these factors can help both employers and applicants manage expectations and improve the efficiency of the process.
1. Company Policies and Size
Larger companies often have more complex systems for handling employment verifications, which can sometimes result in longer wait times. Larger organizations may have centralized HR departments that manage all employment verifications, which may involve multiple levels of approval. Conversely, smaller companies with fewer employees may have a more streamlined verification process but might be slower in responding if the person handling employment verification is unavailable.
- Large Organizations: These companies may have automated systems but can also be slow due to the number of verifications they process.
- Small Businesses: Small companies may be faster to verify, but they may lack an efficient system to handle multiple requests at once.
2. Type of Job and Role
The type of job or role being verified can impact the verification process. Jobs in industries such as healthcare, government, or positions requiring high security clearances may take longer due to the need for additional checks or specialized information. In contrast, verifying a typical office job in a standard industry may be quicker.
- High-Security or Regulated Jobs: These may require extra background checks or verification of qualifications, leading to longer processing times.
- Standard Positions: For less regulated roles, the verification process can be completed more quickly.
3. Method of Verification
The method through which the employment verification is conducted significantly impacts how long the process takes. The three main methods of verification—phone verification, email verification, and third-party verification—each have their advantages and disadvantages in terms of speed.
- Phone Verification: This method is generally the fastest as it allows for direct communication between the verifier and the employer. Phone verifications often take 1-2 business days, depending on the availability of the contact person.
- Email Verification: Email verifications can be slightly slower because they depend on the recipient’s response time. However, they are still relatively fast, usually taking between 1-3 business days. Response times can vary depending on the company’s HR policies and workload.
- Third-Party Verification Services: Using a third-party service for employment verification can take 3-7 business days on average. These services manage the verification process, including reaching out to previous employers, and may require additional time for confirmation, especially if there are discrepancies or incomplete records.
4. Employer Response Time
The most significant factor in the duration of employment verification is the response time of the employer or HR department. Some employers may have a dedicated team to handle verification requests, while others may rely on individual HR staff members who may not prioritize these requests during peak times. If an employer is slow to respond or if additional clarification is needed, the process can be delayed.
- Busy Employers: If an employer has a large number of verification requests or is in a busy period, responses may be slower, extending the time required for the verification process.
- Employers with Clear Records: If the employee’s records are well-maintained and clear, the process is typically faster, as fewer questions or follow-ups are needed.
5. Completeness of the Verification Request
The accuracy and completeness of the information provided by the job applicant can also impact the time it takes for the verification process. If the applicant has provided all necessary documentation, such as their job title, dates of employment, and HR contact details, the process is likely to move faster. Missing or incorrect information can lead to delays as the verifier will need to go back to the applicant for clarification.
- Complete Information: If applicants provide accurate and comprehensive information, the verification process can move more quickly.
- Incomplete Information: When verification requests are missing details, additional time may be needed to gather the correct information.
Tips for Speeding Up the Employment Verification Process
Both employers and applicants can take steps to ensure the verification process moves as smoothly and quickly as possible. Here are some best practices:
For Employers:
- Centralize HR Operations: By centralizing HR and employing standardized processes for employment verification, companies can speed up the overall process.
- Respond Promptly: A quick response to verification requests can prevent delays, especially if the request is time-sensitive.
- Maintain Organized Records: Employers should ensure that their employee records are up-to-date and easily accessible. This will reduce time spent searching for information.
For Applicants:
- Provide Complete Information: Ensure that all the necessary details for the verification process are included in your application or resume. This includes job titles, dates of employment, and HR contact details.
- Notify Your Employer: Inform your employer or former employer in advance if you anticipate a verification request, so they can prepare to respond quickly.
- Follow Up: If the process is taking longer than expected, applicants should follow up with the verifier to check on the status.
Our Services: Efficient and Reliable Employment Verification
At ExactBackgroundChecks.com, we provide reliable, quick, and accurate employment verification services to streamline the process. Whether you’re an employer looking to verify a candidate’s employment history or an applicant in need of fast verification, our services can help.
- Comprehensive Verification: We verify employment history, job titles, dates of employment, and even salary (when applicable).
- Fast Turnaround Times: With our network of verified contacts and streamlined processes, we offer fast verification services, typically within 1-3 business days.
- Secure and Confidential: We adhere to all relevant privacy laws and confidentiality agreements to ensure that your verification process is handled securely and in compliance with legal standards.
By choosing ExactBackgroundChecks.com, you can ensure that employment verifications are completed efficiently, reducing delays and ensuring a smooth transition for new hires or rental applications.
Legal Aspects of Employment Verification
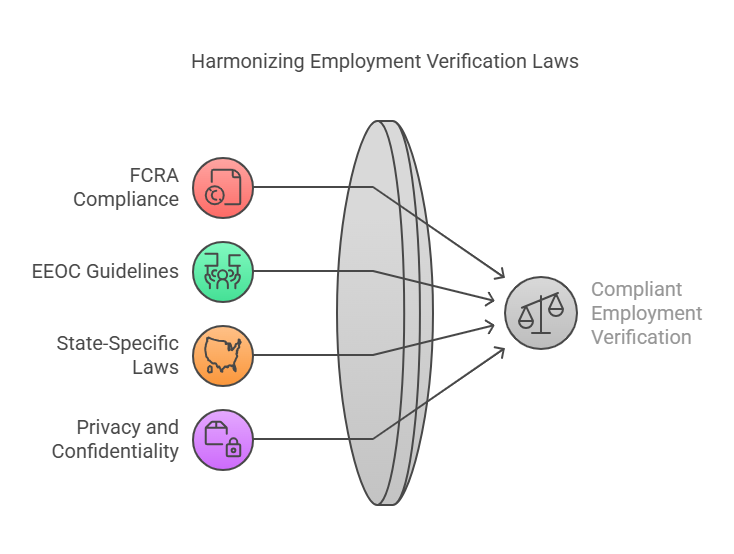
Employment verification is an essential process that requires careful attention to legal standards and regulations. Various laws govern how employment verification must be conducted to ensure compliance and to protect the rights of employees and applicants.
1. Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) Compliance
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) plays a significant role in employment verification, particularly when background checks are involved. The FCRA is a federal law that regulates how personal information is collected, used, and shared by background screening companies. It ensures that employers follow fair practices when requesting employment information, including verifying past employment.
- Applicant Consent: Under the FCRA, employers must obtain written consent from applicants before conducting a background check, including employment verification.
- Notification of Adverse Action: If an employer decides not to hire a candidate based on information obtained through employment verification, the applicant must be notified and provided an opportunity to dispute the findings.
2. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Guidelines
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) enforces federal laws that prohibit employment discrimination. When conducting employment verifications, employers must ensure they comply with the EEOC’s guidelines, which aim to prevent discrimination based on race, gender, disability, or other protected characteristics.
- Non-Discriminatory Practices: Employers should verify employment in a way that does not discriminate against individuals based on any protected class. For example, making hiring decisions based on incomplete or inaccurate verification data can inadvertently lead to discriminatory practices.
- Consistency: Employers must ensure that employment verification is conducted consistently for all candidates to avoid legal challenges related to discrimination.
3. State-Specific Laws
In addition to federal regulations, employers must also comply with state-specific laws when conducting employment verification. Some states may have additional requirements, such as providing specific notice to employees before verifying their employment, or they may have more stringent privacy protections for personal information.
- State Privacy Laws: Some states have more stringent privacy laws than federal regulations. For example, certain states may require employers to maintain stricter control over the use of personal data during the employment verification process.
4. Privacy and Confidentiality
Protecting the privacy and confidentiality of applicants and employees is paramount during the employment verification process. Employers must be cautious when handling sensitive information to avoid potential data breaches or unauthorized disclosures.
- Confidentiality Agreements: It is a good practice for employers and verification agencies to enter into confidentiality agreements that ensure the information shared during the verification process is protected.
- Secure Data Handling: Any personal data, including employment history, should be transmitted through secure channels to protect against unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about employment verification:
What is employment verification?
It's the process of confirming an individual's employment history details, like job title, dates of employment, and salary, typically requested by potential employers, landlords, or financial institutions.
Why is employment verification important?
It confirms the accuracy of job information, assesses reliability, ensures compliance with regulations, and mitigates risks for employers, landlords, and lenders.
How long does employment verification typically take?
On average, it takes 1 to 3 business days, but it can vary depending on factors like company size, verification method, and employer response time.
What are the common methods of employment verification?
Common methods include phone verification (1-2 business days), email verification (1-3 business days), and third-party services (3-7 business days).
What legal aspects should be considered during employment verification?
Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines, state-specific laws, and ensuring privacy and confidentiality.
What is employment verification?
It's the process of confirming an individual's employment history details, like job title, dates of employment, and salary, typically requested by potential employers, landlords, or financial institutions.
Why is employment verification important?
It confirms the accuracy of job information, assesses reliability, ensures compliance with regulations, and mitigates risks for employers, landlords, and lenders.
How long does employment verification typically take?
On average, it takes 1 to 3 business days, but it can vary depending on factors like company size, verification method, and employer response time.
What are the common methods of employment verification?
Common methods include phone verification (1-2 business days), email verification (1-3 business days), and third-party services (3-7 business days).
What legal aspects should be considered during employment verification?
Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines, state-specific laws, and ensuring privacy and confidentiality.
Conclusion
Employment verification is a critical step in the hiring process that ensures employers make informed decisions about prospective employees. By understanding the steps involved and the factors that influence the duration of the verification process, employers can improve their efficiency and manage expectations.
As discussed in this article, it is essential to comply with legal requirements, including those set by the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), to ensure that the employment verification process is both fair and legally compliant.
For employers seeking to streamline their hiring process or applicants looking for assistance with employment verification, services like ExactBackgroundChecks can offer timely and reliable background checks. By utilizing efficient and secure employment verification methods, both parties can ensure that the process runs smoothly, protecting the interests of all involved.