Effective Risk Mitigation Examples and Strategies Across Industries

Understanding Risk Mitigation: A Comprehensive Overview
What is Risk Mitigation?
Risk mitigation is the process of identifying, assessing, and implementing strategies to minimize or manage the potential impact of risks. In both business and personal contexts, risk mitigation aims to reduce the likelihood and severity of negative events that could disrupt operations or harm an organization’s objectives. Risk mitigation is essential for organizations to ensure continuity, safeguard assets, and maintain a stable working environment.
The Importance of Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation is a key element of strategic planning for organizations across all industries. By identifying potential risks and preparing proactive measures, businesses can reduce their vulnerability to disruptions. Effective risk mitigation helps organizations remain resilient in the face of challenges, whether internal or external, and maintain their competitive edge. In essence, risk mitigation allows organizations to anticipate potential issues and minimize their effects on operations.
Types of Risks Organizations Face
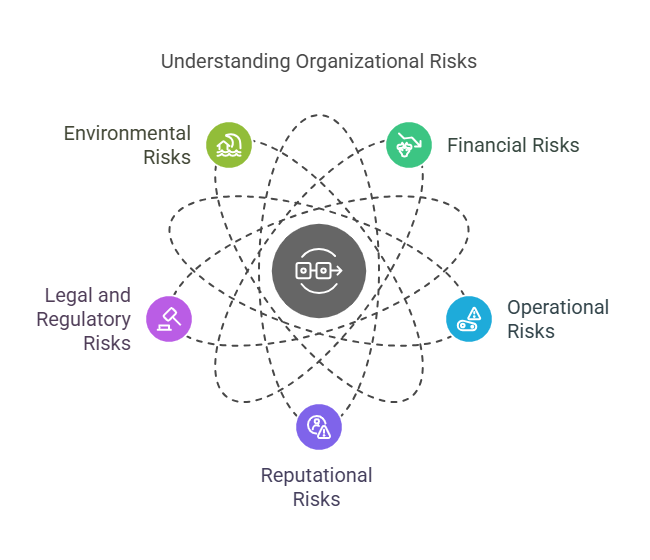
Risk mitigation can be applied to a wide array of risks. Here are the most common categories of risks that organizations typically encounter:
- Financial Risks: These involve uncertainties related to money, investments, or financial performance. Common examples include market fluctuations, interest rate changes, or credit risks that could affect an organization’s profitability.
- Operational Risks: These risks arise from the internal processes, systems, and human resources within an organization. Examples include equipment failures, supply chain disruptions, and employee errors.
- Reputational Risks: These occur when an organization’s image or public perception is damaged, which can result from scandals, poor customer service, or negative media coverage.
- Legal and Regulatory Risks: These risks stem from the legal environment in which a business operates. Compliance with laws and regulations is crucial to avoid penalties, lawsuits, or reputational damage. Examples include issues with labor laws, environmental regulations, or intellectual property rights.
- Environmental Risks: These risks are associated with natural disasters or environmental factors such as floods, earthquakes, and pollution. These can cause severe disruptions to business operations and pose a threat to long-term sustainability.
The Risk Mitigation Process
Risk mitigation is a structured process that involves several key steps to identify, assess, and minimize the impact of risks. The general process is as follows:
- Risk Identification: This step involves recognizing all potential risks that could affect an organization’s operations. It involves brainstorming, consulting experts, and reviewing historical data to pinpoint possible vulnerabilities.
- Risk Assessment: After identifying potential risks, businesses need to evaluate their severity and likelihood. This helps prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurring.
- Risk Control and Mitigation: Once risks have been identified and assessed, businesses implement strategies to mitigate them. This could include preventive actions, contingency plans, or insurance to transfer the risk.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies ensures that the measures put in place remain effective and appropriate over time. Regular reviews also allow organizations to adapt to emerging risks.
Common Risk Mitigation Strategies
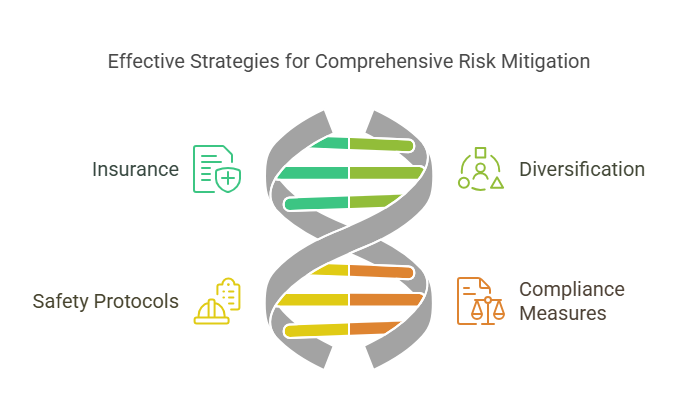
The strategies used to mitigate risks vary depending on the type of risk and the industry in question. Here are some general examples:
- Insurance: One of the most common ways to manage financial and operational risks, insurance provides a safety net to cover the costs of damages, losses, or liabilities.
- Diversification: Businesses can mitigate financial risks by diversifying their investments, products, or services. This ensures that the failure of one product or market does not lead to a complete collapse.
- Safety Protocols and Training: In industries like healthcare and manufacturing, implementing robust safety protocols and employee training programs reduces operational risks and ensures compliance with regulations.
- Compliance Measures: Adhering to industry regulations and standards ensures businesses mitigate legal risks and avoid costly fines or legal disputes.
In the following section, we will explore practical examples of risk mitigation across various industries.
Practical Risk Mitigation Examples Across Industries
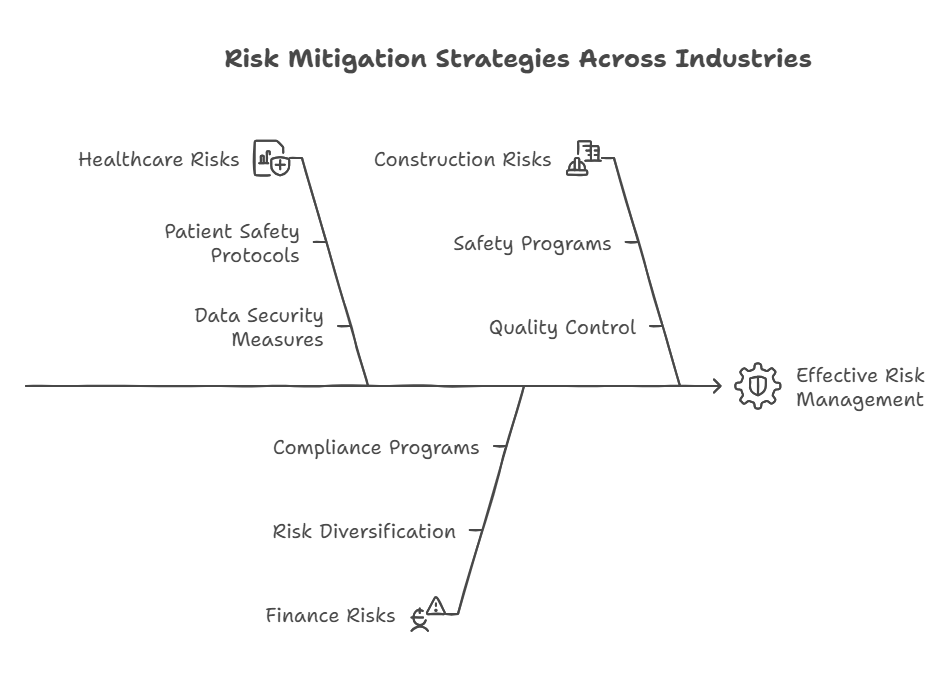
Risk Mitigation in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, risks can have far-reaching consequences, affecting both patient care and an organization’s financial stability. Therefore, healthcare providers implement a range of risk mitigation strategies to ensure patient safety, regulatory compliance, and financial security.
Example 1: Patient Safety and Protocols
Healthcare organizations use strict patient safety protocols to reduce operational risks, such as medical errors or accidents. For example, hospitals often implement standardized checklists for procedures, ensure staff undergo continuous training, and invest in advanced medical technology to prevent misdiagnosis or treatment errors. These efforts help prevent costly lawsuits and maintain patient trust.
Example 2: Data Security
As healthcare providers store sensitive patient data, ensuring the protection of this data is crucial for mitigating legal and reputational risks. Health institutions invest in strong cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, regular audits, and staff training on privacy standards, to comply with healthcare regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and protect patient information from data breaches.
Risk Mitigation in Finance
In the finance industry, managing financial risks and regulatory compliance is critical. The financial sector is highly regulated, and businesses must adapt to ensure compliance while safeguarding investments and assets.
Example 1: Risk Diversification
Banks and investment firms use risk diversification to mitigate financial risks. By spreading investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, financial institutions can reduce the impact of market volatility. In addition, diversification across geographies helps businesses avoid being adversely affected by economic downturns in specific regions.
Example 2: Compliance Programs
Financial institutions have dedicated compliance departments to ensure they follow regulatory requirements. This includes anti-money laundering (AML) measures, Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, and following guidelines set by organizations like the SEC. These strategies mitigate legal risks and ensure businesses avoid penalties and lawsuits.
Risk Mitigation in Construction
The construction industry is inherently risky due to factors like worker safety, project delays, and environmental hazards. Construction companies adopt a variety of strategies to manage these risks.
Example 1: Safety Programs and Insurance
Construction companies implement comprehensive safety training for employees, ensuring they follow industry safety standards. Additionally, construction firms often purchase insurance to cover potential liabilities from worker injuries or property damage. These steps help reduce operational and legal risks.
Example 2: Quality Control and Project Management
Risk mitigation in construction projects also involves adhering to strict quality control measures and project management techniques. Project managers monitor progress, conduct regular inspections, and ensure compliance with building codes to reduce the risk of delays or construction defects.
The Role of Technology in Risk Mitigation
Technology plays a pivotal role in reducing risks across industries. In finance, automation helps to monitor transactions and detect fraudulent activities. In healthcare, electronic health records improve accuracy and reduce errors. Technology-driven solutions like AI and machine learning are increasingly being used for predictive analytics, helping organizations anticipate and mitigate risks before they materialize.
Employment Risk Mitigation via Background Checks
Background checks play a crucial role in mitigating employment-related risks, especially when hiring new employees. Companies often turn to services like exactbackgroundchecks to screen candidates and ensure they have the necessary qualifications, a clean criminal record, and no history of fraudulent behavior. These checks help organizations avoid costly hiring mistakes and protect themselves from potential legal or reputational risks.
Legal Aspects of Risk Mitigation
Adhering to legal requirements is essential for effective risk mitigation. Failure to comply with laws can expose an organization to fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage. In particular, businesses should ensure they follow workplace safety regulations, financial reporting requirements, and industry-specific laws. Regular audits, employee training, and staying up-to-date with relevant regulations are crucial steps in ensuring compliance and mitigating legal risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between risk mitigation and risk management?
Risk mitigation is a subset of risk management. While risk management encompasses the entire process of identifying, assessing, and addressing risks, mitigation specifically focuses on strategies to minimize the likelihood or impact of those risks. In essence, risk mitigation is the actionable phase of the broader risk management framework.
How can small businesses implement effective risk mitigation strategies?
Small businesses can adopt effective risk mitigation strategies by:
- Conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities.
- Prioritizing cost-effective solutions, such as insurance for key assets.
- Investing in training and resources to build internal capabilities.
- Leveraging technology, such as cloud-based risk management tools, to streamline processes.
- Seeking expert advice or outsourcing risk mitigation functions to specialized providers like Exact Background Checks.
What tools are available for tracking and assessing risks?
Numerous tools and platforms are designed to assist with risk assessment and mitigation:
- Project Management Software: Tools like Trello or Asana help track project-related risks.
- Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Platforms: Software such as LogicManager or Resolver provides comprehensive solutions for identifying and mitigating risks.
- Cybersecurity Solutions: Firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption tools address IT-related risks.
- Background Screening Services: Companies like Exact Background Checks offer services to verify employment, criminal history, and other critical data to reduce hiring risks.
Can risk mitigation eliminate all risks?
No, risk mitigation cannot eliminate all risks. Some risks are inherent and cannot be entirely avoided or reduced. The goal of mitigation is to manage risks to a tolerable level, ensuring that their impact is minimized and does not disrupt organizational or personal objectives.
How does Exact Background Checks contribute to reducing employment-related risks?
Exact Background Checks helps employers mitigate risks associated with hiring by:
- Verifying employment history, credentials, and criminal records.
- Ensuring compliance with legal requirements such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
- Providing accurate and timely reports to support informed decision-making.
By leveraging our services, businesses can build trustworthy teams while minimizing legal and reputational risks.
Conclusion
Risk mitigation is an essential process that every organization must embrace to protect its assets, maintain its reputation, and ensure legal compliance. By identifying potential risks and implementing effective strategies, businesses can reduce vulnerabilities and achieve long-term success. Whether through technology, employee training, or thorough background checks, risk mitigation plays a crucial role in safeguarding business operations.