How to Ensure Accurate Urinalysis Drug Test

Understanding the Urinalysis Drug Test
A urinalysis drug test is a diagnostic procedure used to detect the presence of drugs or their metabolites in an individual’s urine. This method has become one of the most common and reliable ways to screen for drug use across various settings, such as the workplace, law enforcement, healthcare, and more. Whether it’s for employment purposes, probation monitoring, or medical diagnostics, a urinalysis drug test serves as a crucial tool in maintaining safety, compliance, and public health.
What Is a Urinalysis Drug Test?
A urinalysis drug test is a form of screening that identifies substances like marijuana, cocaine, opioids, methamphetamines, and other commonly abused drugs in urine samples. The test is simple, non-invasive, and relatively inexpensive, making it a popular choice for employers and medical professionals alike.
During the procedure, an individual provides a urine sample, which is then analyzed to detect traces of drugs or their byproducts (metabolites). These metabolites are substances that are created when the body processes drugs, and they remain in the urine for varying lengths of time depending on the substance and how it is metabolized.
How Does a Urinalysis Drug Test Work?
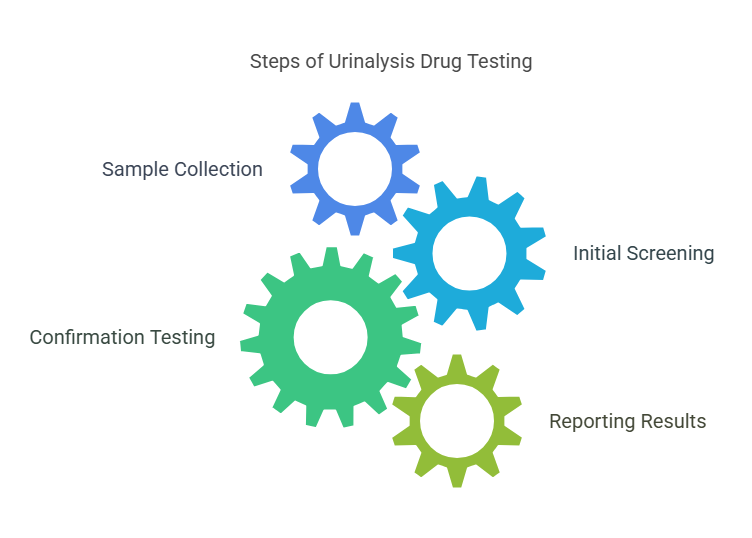
The process for a urinalysis drug test is straightforward. Here is a basic outline of how the test is typically conducted:
- Sample Collection: The individual provides a urine sample in a clean container, usually under the supervision of a medical professional to ensure the sample is valid and untampered.
- Initial Screening: The sample is tested using an immunoassay technique, which detects the presence of specific drug metabolites in the urine.
- Confirmation Testing: If the initial test results are positive, the sample may undergo Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) or another more accurate technique for confirmation.
- Reporting Results: The results are typically available within a few days, depending on the testing method used. The result is classified as positive, negative, or inconclusive.
Advantages of Urinalysis Drug Testing
The urinalysis drug test is favored for several reasons:
- Ease of Collection: It is non-invasive, requiring only a urine sample, which is easier and less stressful than blood or hair tests.
- Cost-Effective: Urinalysis is relatively inexpensive compared to other testing methods, making it an affordable option for widespread screening.
- Non-Invasive: Urinalysis does not require needles or specialized equipment, which makes it less invasive and more comfortable for the individual being tested.
- Accurate Detection: The test is highly effective in detecting drug use and can identify metabolites that remain in the urine for days or even weeks, depending on the drug.
Common Scenarios for Urinalysis Drug Testing
Urinalysis drug tests are used in a variety of scenarios. Some of the most common include:
- Employment Screening: Many employers use urinalysis drug tests as part of their pre-employment or ongoing screening process to ensure a drug-free workplace.
- Probation and Parole Monitoring: Individuals on probation or parole may be required to undergo regular urinalysis drug tests to ensure compliance with their legal agreements.
- Sports Testing: Athletes are often subjected to drug tests to maintain fair play and prevent the use of performance-enhancing drugs.
- Healthcare: Medical professionals may order a urinalysis drug test to monitor patients who are receiving treatment for substance abuse or are suspected of drug use.
- Legal or Custody Cases: Urinalysis drug tests are commonly used in legal proceedings to determine custody arrangements or assess a person’s fitness for certain responsibilities.
Types of Urinalysis Drug Tests
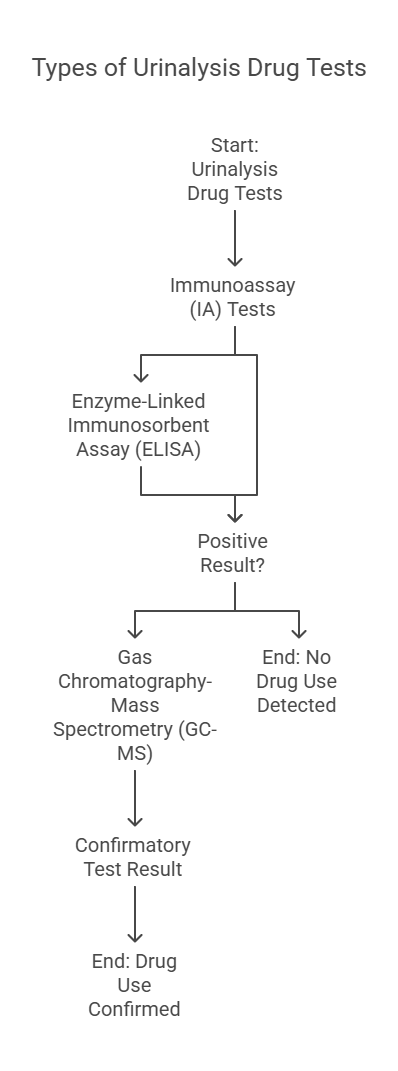
There are several types of urinalysis drug tests, each offering unique benefits and varying levels of accuracy. These tests utilize different methodologies to detect drug metabolites in the urine sample, which can help determine whether someone has used specific substances. Let’s dive into the most commonly used types of urinalysis drug tests:
- Immunoassay (IA) Tests
The Immunoassay (IA) test is one of the most common techniques used in urinalysis drug testing. This method works by detecting drug metabolites through the interaction of the sample with antibodies that specifically bind to the metabolites of various drugs.
- How It Works: The test involves mixing the urine sample with antibodies that react with metabolites. If the drug is present in the sample, the reaction will indicate a positive result.
- Advantages: IA tests are quick, cost-effective, and easy to perform. They are often used as an initial screening test because they provide rapid results.
- Limitations: While immunoassays are reliable, they can produce false positives or false negatives. This is why confirmatory testing is necessary in certain cases.
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
When an Immunoassay (IA) test shows a positive result, a Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) test is often conducted to confirm the findings. GC-MS is a more precise and accurate method used to identify the specific compounds present in the urine sample.
- How It Works: GC-MS separates the components in a urine sample based on their molecular weight and structure. It then analyzes these components, identifying the presence of specific drug metabolites.
- Advantages: GC-MS is highly accurate, and it can definitively confirm the presence of drugs in the system, making it the gold standard for drug testing.
- Limitations: GC-MS testing is more expensive and time-consuming compared to other methods, which is why it is typically used only as a confirmatory test.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is another form of immunoassay, but it works by detecting drug metabolites using a different mechanism.
- How It Works: ELISA uses an enzyme to bind to drug metabolites in the urine sample. The presence of metabolites triggers a color change, indicating a positive or negative result.
- Advantages: ELISA is relatively easy to perform and is used for detecting specific substances, such as marijuana, opiates, cocaine, and amphetamines.
- Limitations: Similar to other immunoassay methods, ELISA is less accurate than GC-MS and can also result in false positives or negatives.
Process of Urinalysis Drug Testing
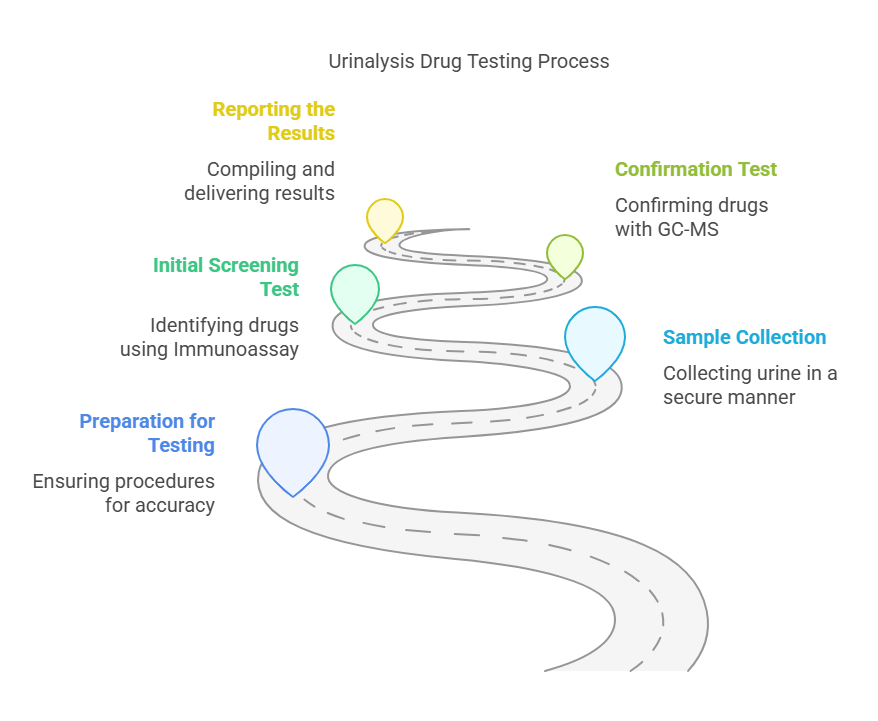
The process of urinalysis drug testing typically follows a standard procedure that ensures the integrity of the test and accurate results. Here’s an outline of the steps involved:
- Preparation for Testing
Before the urinalysis drug test takes place, both the individual being tested and the testing agency must follow specific procedures to ensure accuracy. For instance:
- Chain of Custody: The test must be conducted in a manner that prevents tampering with the urine sample. A chain of custody is maintained to track the sample from collection to analysis.
- Instructions for Participants: The individual undergoing the test may be instructed to drink a certain amount of water before providing the sample to ensure a sufficient quantity. However, excessive fluid intake can be discouraged, as it may dilute the sample.
- Sample Collection
The individual provides a urine sample, which is typically collected in a clean container. In some situations, the individual may be asked to provide the sample in a secure, monitored setting to prevent sample adulteration or substitution.
- Temperature Monitoring: The sample is immediately tested for temperature to ensure that it was freshly collected and has not been tampered with.
- Initial Screening Test
The sample is initially tested using an Immunoassay (IA) or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). This step identifies any drugs or their metabolites in the urine.
- Confirmation Test
If the initial test result is positive, the sample undergoes Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) to confirm the presence of specific drugs and eliminate the risk of false positives.
- Reporting the Results
Once the testing is complete, the results are compiled and provided to the requesting party. Results are usually classified as positive, negative, or inconclusive. A positive result means the individual tested has used the substance(s) being screened for, while a negative result indicates no drugs were detected. Inconclusive results may require further investigation or retesting.
Challenges and Limitations of Free vs. Paid Drug Testing Services
While free public drug testing services are available, they may not offer the same level of accuracy and detail as paid, professional drug testing services like those provided by Exact Background Checks. Here are some key differences between the two:
| Aspect | Free Public Drug Testing | Paid Professional Drug Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Can be prone to false positives/negatives | High accuracy with confirmation testing (e.g., GC-MS) |
| Results Turnaround | May take longer and be less reliable | Quick and reliable results, often within 24-48 hours |
| Substances Tested | Limited substances detected | Comprehensive drug panels, including a wide variety of drugs |
| Test Confirmation | Typically no confirmation test | Includes confirmation tests (e.g., GC-MS) for all positives |
| Legal and Compliance | May not follow all regulatory guidelines | Strict adherence to legal and regulatory standards |
Exact Background Checks: Professional Urinalysis Drug Testing Services
Exact Background Checks offers comprehensive drug testing services that go beyond what free public services provide. Our testing procedures are fully compliant with legal standards, and we offer a wide range of drug screening options to meet your needs. Whether you need pre-employment drug testing, routine screening for existing employees, or testing for other purposes, our services are accurate, reliable, and confidential.
Legal Aspects of Urinalysis Drug Testing
Urinalysis drug testing is governed by various laws and regulations that ensure the rights of individuals are protected, while also ensuring that employers and other organizations can screen for drug use in a lawful and ethical manner. Here are some key legal aspects of urinalysis drug testing:
1. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Drug Testing
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides protection to individuals with disabilities, and it also plays a role in drug testing, particularly in the workplace. Under the ADA, employers are allowed to conduct drug tests but must follow specific guidelines to ensure they are not discriminating against individuals with disabilities.
- What the ADA allows: Employers can test for drugs as part of pre-employment screening, random testing, or post-accident testing. However, employers must ensure they do not unfairly target individuals based on their disability status.
- Important Consideration: The ADA does not protect individuals from drug testing. Employers may exclude candidates who test positive for illegal substances or who are unable to perform essential job functions due to drug use.
2. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a federal law that protects individuals’ health information. While urinalysis drug testing is often conducted for employment purposes, it also has health implications, particularly if the test is performed for medical reasons or during a healthcare visit.
- Privacy Protections: HIPAA ensures that individuals’ drug test results are kept confidential and are shared only with authorized entities.
- Informed Consent: The individual being tested must provide informed consent before undergoing a drug test. This includes acknowledging that their test results will be used and shared according to relevant laws and regulations.
3. State and Federal Laws Governing Drug Testing
Laws surrounding urinalysis drug testing can vary between states, and each state has its own set of rules regarding how, when, and where drug testing can occur. Here are some factors to consider:
- Informed Consent: In most states, employers must obtain consent from employees or job applicants before conducting drug tests.
- Notice: Employers may be required to provide notice about drug testing policies and practices as part of the hiring process or in employee handbooks.
- Ban the Box Laws: Certain states have enacted “ban the box” laws, which prohibit employers from asking about criminal history or drug use on job applications. These laws impact how and when drug testing can be implemented in the hiring process.
4. Expungement and Its Impact on Drug Testing Results
An individual’s criminal history, including past drug offenses, can affect the results of urinalysis drug tests in certain scenarios. Expungement is a legal process that allows individuals to have certain criminal records removed from public access.
- Impact on Drug Test Results: While expungement may clear a person’s criminal history, it does not affect the results of a drug test. Drug tests detect the presence of drug metabolites in the body and do not take into account past criminal convictions.
- Legal Implications: An employer may not use expunged records in making hiring decisions, but they may still be required to conduct a drug test if company policies or regulatory requirements mandate it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Urinalysis Drug Testing
How long does marijuana stay in your system for a urinalysis drug test?
- The amount of time marijuana stays in the system depends on several factors, such as frequency of use, body fat, and metabolism. For occasional users, marijuana may be detectable in urine for 1-3 days, while for heavy users, it could be detectable for up to 30 days or longer.
Can a positive urinalysis drug test result be contested?
- Yes, a positive drug test result can be contested. If a person believes the test result is inaccurate, they may request a confirmatory test using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) to ensure accuracy. Additionally, individuals can appeal the results based on specific circumstances, such as medications that may have led to a false positive.
What happens if a drug test comes back inconclusive?
- If a drug test result is inconclusive, the sample is typically retested or a new sample may be requested. This can occur due to issues like sample contamination, insufficient quantity, or errors in the initial test. The individual may be asked to provide a fresh sample for testing.
How accurate is a urinalysis drug test?
- Urinalysis drug tests are highly accurate when performed properly. However, they are not foolproof and can occasionally result in false positives or false negatives. The use of confirmation tests like GC-MS significantly reduces the risk of inaccurate results.
What substances are commonly tested for in a urinalysis drug test?
- A urinalysis drug test typically screens for a range of substances, including:
- Marijuana (THC)
- Cocaine
- Opiates (e.g., heroin, morphine)
- Amphetamines (e.g., methamphetamine, MDMA)
- Phencyclidine (PCP)
- Benzodiazepines
- Barbiturates
Tests can also be customized based on the substances relevant to the industry or specific requirements of an organization.
Conclusion
Urinalysis drug testing plays a crucial role in various industries, including workplaces, law enforcement, and healthcare, by ensuring that individuals comply with policies regarding drug use. From understanding the different types of drug tests to addressing the legal implications of conducting such tests, it’s essential to navigate this process carefully.
While urinalysis drug tests are reliable, the accuracy and effectiveness of these tests can vary depending on the methods used and whether confirmatory testing is conducted. By choosing Exact Background Checks for your drug testing needs, employers, organizations, and individuals can benefit from comprehensive, efficient, and legally compliant drug testing services. Whether for pre-employment screening, random testing, or other scenarios, we provide high-quality testing solutions to help maintain a safe and productive environment.