Common Disqualifiers in Federal Employment Background Checks

Introduction and Overview of Federal Employment Background Checks
Federal employment comes with significant responsibilities that often require a high level of trust, integrity, and competence. To ensure that candidates meet these standards, federal agencies conduct federal employment background checks as a critical step in the hiring process. These background checks help verify an applicant’s qualifications, evaluate potential risks, and uphold the safety and security of government operations.
What Is a Federal Employment Background Check?
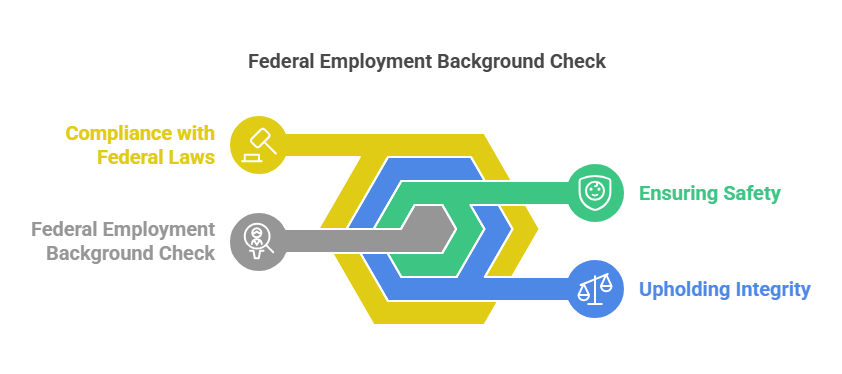
A federal employment background check is a comprehensive review of an applicant’s personal, professional, and financial history to determine their suitability for a federal position. Unlike standard background checks used in private-sector hiring, federal checks are more detailed and tailored to meet the stringent requirements of federal roles.
Key Objectives of a Federal Background Check
- Ensuring Safety: Federal positions often involve access to sensitive information or critical systems, making it essential to screen candidates for any potential security risks.
- Upholding Integrity: These checks help identify any past behaviors, such as falsification of documents or criminal activity, that could undermine the integrity of government operations.
- Compliance with Federal Laws: Federal agencies must adhere to strict legal and ethical standards, ensuring that all hires meet the necessary criteria.
Why Are Federal Employment Background Checks Required?
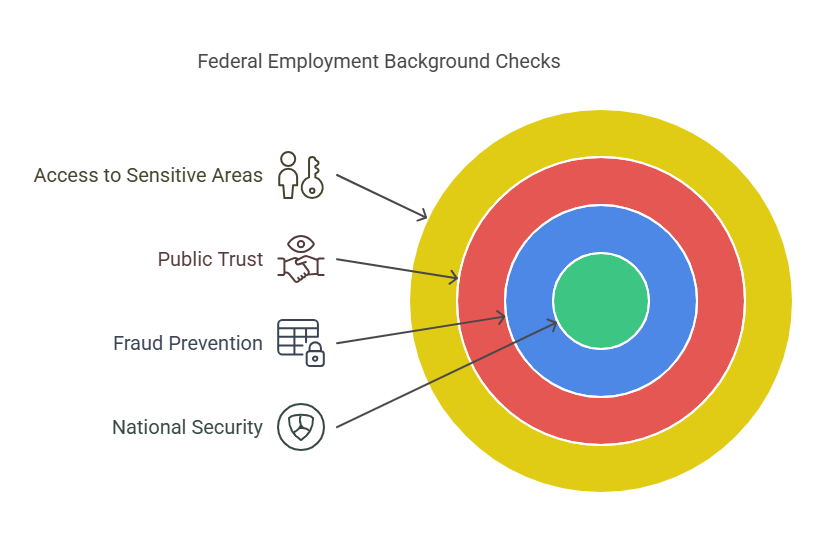
Federal agencies operate in fields that directly impact public welfare, national security, and the effective functioning of government institutions. From law enforcement to administrative roles, federal employees may have access to:
- Classified information.
- Government funds and resources.
- Public infrastructure or sensitive programs.
As a result, federal employment background checks are designed to:
- Protect national security.
- Prevent fraud, theft, or other unethical behaviors.
- Maintain public trust in government institutions.
For instance, a position within the Department of Defense may require a security clearance, while roles at the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) might involve verifying the financial responsibility of applicants.
Components of a Federal Employment Background Check
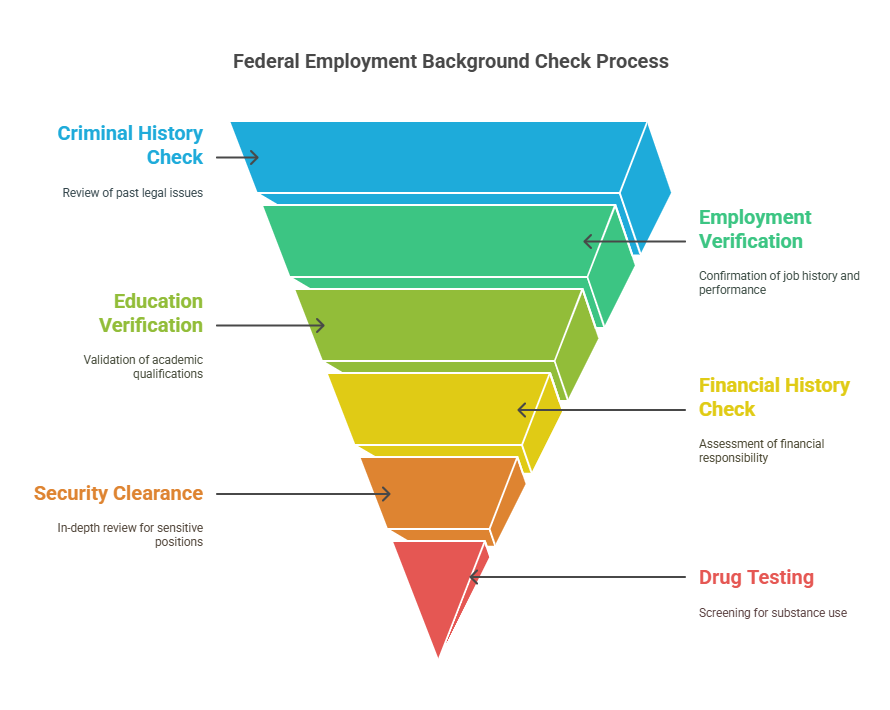
Federal employment background checks are more comprehensive than standard screenings and typically include multiple components to evaluate a candidate’s overall suitability. Below are the common elements of these checks:
1. Criminal History Check
Federal agencies conduct detailed criminal background checks to identify any past arrests, convictions, or pending charges. They may access local, state, and federal criminal databases to verify records. Certain crimes, such as felonies or offenses involving dishonesty, can disqualify candidates from federal employment.
2. Employment Verification
Verifying a candidate’s employment history is critical to ensure that the information provided on their application is accurate. Federal background checks often confirm:
- Previous job titles.
- Employment dates.
- Reasons for leaving prior positions.
- Job performance and professional conduct.
3. Education Verification
Federal positions often require specific educational qualifications. Background checks verify academic credentials, such as degrees, certifications, and transcripts, to ensure authenticity.
4. Financial History Check
Financial responsibility is an important criterion for many federal jobs, particularly those involving money management or security clearance. A financial history check may include:
- Credit reports.
- Bankruptcy filings.
- Outstanding debts or liens. Poor financial management or significant debt may indicate a higher risk of susceptibility to bribery or fraud.
5. Security Clearance
Many federal positions require a security clearance, which involves an additional layer of screening. The level of clearance (Confidential, Secret, or Top Secret) dictates the depth of the investigation. Security clearance checks may include:
- A review of criminal and financial history.
- Interviews with personal references.
- Verification of foreign contacts or affiliations.
6. Drug Testing
Drug testing is a common component of federal background checks, ensuring that candidates adhere to drug-free workplace policies. Pre-employment drug tests typically screen for substances such as marijuana, cocaine, opioids, and amphetamines.
7. Reference Checks
Federal agencies often contact personal and professional references to gather insights about a candidate’s character, behavior, and suitability for the role.
How Federal Background Checks Differ from Private Sector Checks
While private-sector employers may conduct basic background screenings, federal employment background checks are far more rigorous. Key differences include:
- Scope: Federal checks delve deeper into personal history, often including checks for financial responsibility and security clearance.
- Duration: Due to their thorough nature, federal background checks may take weeks or even months to complete.
- Standardization: Federal agencies follow strict guidelines set by federal laws and executive orders, ensuring consistency and fairness in the hiring process.
Who Conducts Federal Background Checks?
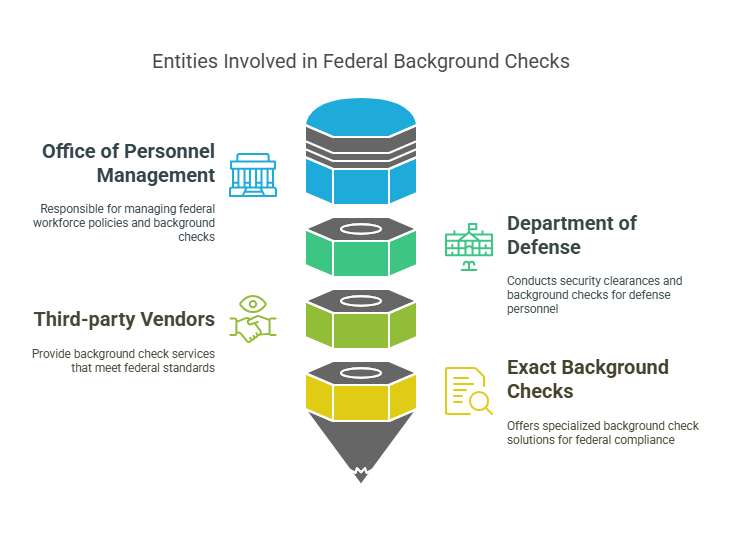
Federal background checks are typically conducted by authorized agencies or contractors specializing in government employment screenings. These include organizations like:
- The Office of Personnel Management (OPM).
- The Department of Defense (DoD).
- Third-party vendors that comply with federal standards.
Additionally, companies like Exact Background Checks play a crucial role in providing reliable background check solutions tailored to meet federal requirements.
The Importance of Federal Employment Background Checks
Federal employment background checks are not just procedural formalities—they are essential for maintaining the safety, security, and efficiency of government operations. By carefully vetting candidates, federal agencies can:
- Ensure that employees uphold the highest ethical and professional standards.
- Minimize risks associated with fraud, security breaches, or other misconduct.
- Protect public resources and maintain citizens’ trust in the government.
In summary, federal background checks are an indispensable tool for safeguarding national security and ensuring the integrity of federal workplaces.
With this foundational understanding of federal employment background checks, the next section will dive deeper into the common disqualifiers that may prevent candidates from securing a federal position.
Common Disqualifiers for Federal Employment and Our Services
Federal employment background checks aim to ensure that candidates meet the rigorous standards required for public service. While these checks are necessary to protect the integrity of federal workplaces, certain issues may arise during the screening process that disqualify individuals from federal employment. This section explores the most common disqualifiers and highlights how organizations like Exact Background Checks assist candidates and employers with reliable background check solutions.
What Are Federal Employment Disqualifiers?
A federal employment disqualifier is any factor uncovered during a background check that renders a candidate ineligible for a federal position. These disqualifiers are based on federal laws, agency-specific regulations, and the requirements of specific job roles. While disqualifiers vary depending on the position, the following are the most common.
Common Disqualifiers for Federal Employment
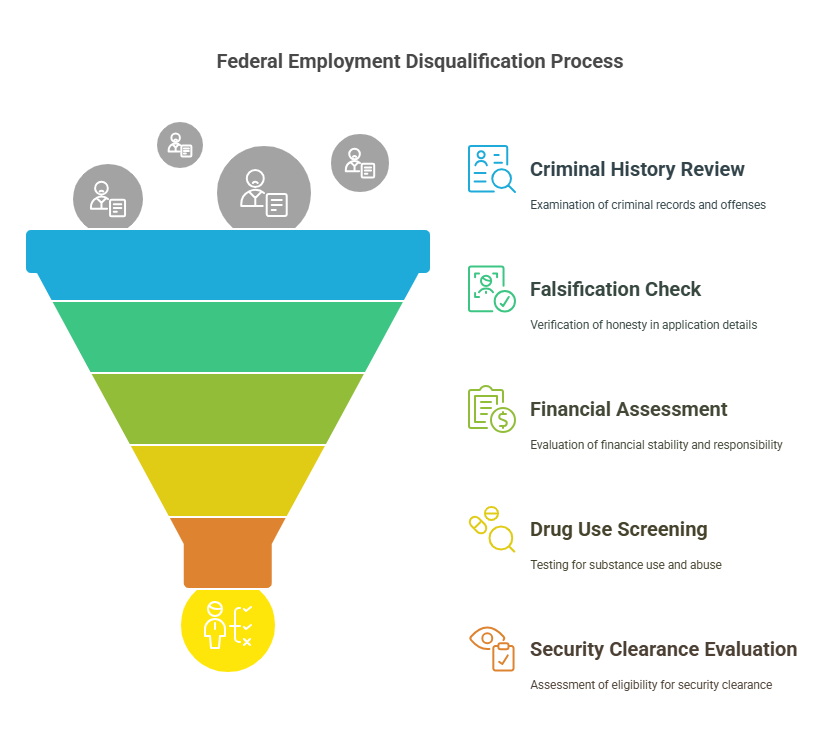
1. Criminal History
A candidate’s criminal record is one of the most significant factors reviewed during a federal background check. The presence of certain convictions or offenses can disqualify an individual, especially if the crimes raise concerns about trustworthiness or integrity.
Disqualifying Criminal Offenses
- Felonies: Convictions for serious crimes such as fraud, embezzlement, or violent offenses often lead to disqualification.
- Misdemeanors: While less severe, some misdemeanors—such as theft or drug-related offenses—may still raise red flags.
- Sex Offender Status: Registered sex offenders are typically disqualified from federal employment.
- Repeat Offenses: A pattern of criminal behavior can indicate a lack of rehabilitation or accountability.
Impact on Security Clearance
Criminal convictions are especially scrutinized in positions requiring security clearance. Certain offenses may permanently bar candidates from obtaining clearance, which is often a prerequisite for federal roles.
2. Falsification of Information
Honesty and transparency are critical in federal employment. Providing false or misleading information during the application process is a major disqualifier.
Examples of Falsification
- Misrepresenting academic credentials or work history.
- Omitting past criminal convictions.
- Fabricating references or certifications.
Federal agencies have zero tolerance for dishonesty, as it reflects poorly on a candidate’s integrity and trustworthiness.
3. Financial Issues
A candidate’s financial history is closely examined during a federal background check, especially for positions involving access to funds or classified information. Poor financial management can be seen as a potential risk for corruption or bribery.
Disqualifying Financial Red Flags
- Bankruptcy: While not always disqualifying, a history of multiple bankruptcies may indicate financial irresponsibility.
- Unpaid Debts or Liens: Significant unresolved debts can raise concerns about a candidate’s ability to manage responsibilities.
- Poor Credit Score: While not a direct disqualifier, a low credit score may prompt further investigation.
4. Drug Use
Drug use is a serious concern for federal employers, particularly in roles that involve public safety or national security. Many agencies enforce strict drug-free workplace policies.
Disqualifying Drug-Related Factors
- Recent Drug Use: Using illegal substances within a specified time frame (e.g., 12 months) is often disqualifying.
- Positive Drug Test Results: Pre-employment drug screening that detects prohibited substances may immediately disqualify a candidate.
- Past Substance Abuse: While past drug use may not automatically disqualify someone, repeated or severe instances can be concerning.
Some federal agencies, such as the Department of Transportation, have specific guidelines regarding drug testing and cutoff levels for disqualification.
5. Security Clearance Concerns
Many federal positions require candidates to obtain a security clearance, which involves a thorough background investigation. Failing to meet clearance requirements is a common disqualifier for federal employment.
Factors That May Prevent Security Clearance
- Foreign Contacts: Significant, unexplained ties to foreign nationals can raise concerns about espionage or loyalty.
- Substance Abuse: A history of substance abuse, particularly when combined with other disqualifiers, may prevent clearance approval.
- Criminal Activity: Convictions for serious crimes are often incompatible with security clearance requirements.
- Inconsistent Information: Providing conflicting or incomplete details during the clearance process may result in disqualification.
6. Poor Employment or Professional History
Federal agencies place a strong emphasis on work ethics and reliability. A poor professional history can disqualify candidates if it suggests they may not perform their duties effectively.
Employment Issues That May Lead to Disqualification
- Terminations for Misconduct: Being fired for ethical breaches or poor performance.
- Job Hopping: Frequent changes in employment without valid reasons.
- Negative References: Unfavorable feedback from past employers or supervisors.
7. Citizenship and Residency Requirements
Most federal positions require U.S. citizenship or permanent residency. Non-compliance with these requirements is an automatic disqualifier for many roles.
How Exact Background Checks Can Help
At Exact Background Checks, we specialize in providing comprehensive background check solutions tailored to federal employment standards. Our services are designed to assist both candidates and employers in navigating the complex requirements of federal screenings.
Our Key Services
- Comprehensive Background Screening: We conduct detailed checks on criminal history, employment verification, education, and financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Drug Testing Solutions: Our reliable drug testing services help employers maintain drug-free workplaces while adhering to federal regulations.
- Security Clearance Assistance: We support candidates and employers with the documentation and processes required for security clearance investigations.
- Compliance Expertise: Our team ensures that all background checks align with federal laws, such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA).
By partnering with us, federal agencies and private contractors can streamline the hiring process, reduce risks, and maintain high standards of integrity.
In the next section, we’ll explore the legal aspects of federal background checks, answer frequently asked questions, and summarize the key takeaways.
Legal Aspects, FAQs, and Conclusion
Federal employment background checks are subject to stringent legal guidelines to ensure compliance, fairness, and respect for candidate rights. This section delves into the legal framework governing these checks, addresses frequently asked questions, and concludes with key takeaways on federal employment background check disqualifiers.
Legal Aspects of Federal Employment Background Checks
1. Compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) governs how background checks are conducted, ensuring that candidates are informed about the process and have an opportunity to dispute inaccuracies. Key requirements under the FCRA include:
- Disclosure and Authorization: Employers must provide candidates with a written notice and obtain their consent before conducting a background check.
- Adverse Action Notification: If a disqualifier is found, candidates must be notified before any adverse employment decision is made.
- Access to Reports: Candidates have the right to review the background check report and dispute any errors.
2. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) Guidelines
The EEOC ensures that background checks do not lead to discriminatory hiring practices. Employers must:
- Avoid blanket disqualification policies (e.g., excluding anyone with a criminal record).
- Assess each case individually, considering the nature of the offense, its relevance to the job, and how much time has passed.
3. Security Clearance Regulations
For positions requiring security clearance, candidates must comply with guidelines set by agencies like the Department of Defense (DoD) or the Office of Personnel Management (OPM). These regulations mandate detailed investigations into:
- Criminal history.
- Financial stability.
- Loyalty and trustworthiness (e.g., foreign ties or allegiance).
4. Privacy Laws
Federal employers must respect candidate privacy by:
- Limiting access to sensitive personal information.
- Using secure methods for collecting and storing data.
- Refraining from asking about non-job-related personal details.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a federal employment background check, and why is it required?
A federal employment background check is a comprehensive review of an applicant's history to determine suitability for a federal position. It's required to ensure safety, uphold integrity, comply with federal laws, and protect national security.
What are the common components of a federal employment background check?
Common components include criminal history checks, employment verification, education verification, financial history checks, security clearance investigations, drug testing, and reference checks.
How do federal background checks differ from private sector checks?
Federal checks are more rigorous, with a broader scope (including financial responsibility and security clearance), longer duration, and strict standardization following federal laws and executive orders.
What are some common disqualifiers for federal employment?
Common disqualifiers include criminal history (felonies, sex offender status), falsification of information, financial issues (bankruptcy, unpaid debts), drug use, security clearance concerns, poor employment history, and non-compliance with citizenship/residency requirements.
What are the key legal aspects of federal employment background checks?
Key legal aspects include compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines, security clearance regulations, and privacy laws.
What is a federal employment background check, and why is it required?
A federal employment background check is a comprehensive review of an applicant's history to determine suitability for a federal position. It's required to ensure safety, uphold integrity, comply with federal laws, and protect national security.
What are the common components of a federal employment background check?
Common components include criminal history checks, employment verification, education verification, financial history checks, security clearance investigations, drug testing, and reference checks.
How do federal background checks differ from private sector checks?
Federal checks are more rigorous, with a broader scope (including financial responsibility and security clearance), longer duration, and strict standardization following federal laws and executive orders.
What are some common disqualifiers for federal employment?
Common disqualifiers include criminal history (felonies, sex offender status), falsification of information, financial issues (bankruptcy, unpaid debts), drug use, security clearance concerns, poor employment history, and non-compliance with citizenship/residency requirements.
What are the key legal aspects of federal employment background checks?
Key legal aspects include compliance with the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines, security clearance regulations, and privacy laws.
Key Takeaways and Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
- Importance of Federal Background Checks: These checks ensure the integrity, security, and efficiency of federal operations.
- Common Disqualifiers: Issues like criminal history, falsified information, financial instability, and drug use can disqualify candidates.
- Legal Compliance: Employers must adhere to federal laws such as the FCRA and EEOC guidelines to ensure fairness and transparency.
The Role of Exact Background Checks
At Exact Background Checks, we understand the complexity and importance of federal employment screenings. Our tailored services help employers comply with legal requirements and make informed hiring decisions while supporting candidates through a fair and transparent process.
Final Thoughts
Federal employment background checks play a pivotal role in maintaining the safety, security, and credibility of government institutions. By understanding the disqualifiers, legal considerations, and candidate rights, both employers and job seekers can navigate the process more effectively.
Proper screening practices are not just about meeting regulations—they are about building a trustworthy and competent federal workforce that serves the public with integrity and dedication.