A Guide to Employment Verification in Mortgage Lending

Understanding Employment Verification for Mortgage Applications
When it comes to applying for a mortgage, one of the most important factors lenders look at is the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. Lenders want to be assured that borrowers have a steady and reliable source of income that will allow them to make timely mortgage payments each month. As a result, employment verification is a crucial part of the mortgage application process.
Employment verification is used to confirm an applicant’s employment status, income, and employment history, which helps lenders assess the borrower’s financial stability. Without proper verification, lenders cannot accurately determine whether the borrower is in a position to meet the financial commitments associated with a mortgage. This process plays a vital role in ensuring the borrower is capable of handling the responsibilities of homeownership while protecting the lender from taking on unnecessary risk.
In this section, we will explore the importance of employment verification in the mortgage process, why it’s necessary, and the methods lenders use to verify employment. We’ll also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
What is Employment Verification for Mortgages?

Employment verification for mortgages refers to the process through which lenders confirm an applicant’s current employment status, income level, and job history. This process is critical because it helps the lender evaluate the applicant’s ability to consistently make monthly mortgage payments based on their income.
The primary purpose of employment verification in mortgage applications is to reduce the risk for the lender by ensuring that the applicant has a stable income source to handle the financial obligations associated with owning a home. This verification is also necessary for the lender to calculate important figures such as the applicant’s debt-to-income ratio (DTI) and to evaluate whether the applicant qualifies for the mortgage amount they are seeking.
Employment verification ensures that the borrower is not only employed but also earns enough income to maintain consistent mortgage payments. Moreover, the verification process helps uncover any discrepancies in the application or employment history that might raise red flags for the lender.
Why Do Lenders Require Employment Verification?
Lenders request employment verification for several key reasons. Let’s take a closer look at the most important factors:
1. Income Stability
Lenders want to make sure the borrower has a steady and reliable income source. A consistent income stream demonstrates the borrower’s ability to make monthly mortgage payments on time. For example, an applicant who has been employed with the same company for several years is often considered a more stable borrower than someone who frequently changes jobs.
2. Loan Qualification
Employment verification helps lenders determine whether an applicant qualifies for a mortgage by assessing their income. Lenders use a borrower’s income to calculate their debt-to-income ratio (DTI), which is a crucial metric for loan approval. The DTI ratio compares the borrower’s total monthly debt payments (including the proposed mortgage) to their gross monthly income. The lower the DTI ratio, the more likely the borrower is to qualify for a mortgage.
3. Risk Assessment
Lenders need to assess the borrower’s financial risk. Without proper employment verification, lenders may be unable to make an accurate judgment about an applicant’s ability to repay the mortgage. Employment verification helps reduce the risk for the lender by providing insight into the borrower’s income consistency and financial stability. Inaccurate or falsified information could lead to approval for individuals who are not financially capable of handling the mortgage, which could result in loan defaults.
4. Fraud Prevention
Employment verification also helps prevent mortgage fraud, where borrowers may provide false information about their employment or income to gain loan approval. For instance, applicants might submit fake pay stubs or tax documents to make it appear as though they are earning more than they actually are. By verifying employment directly with employers or using third-party verification services, lenders can ensure that the applicant’s income and employment status are accurate.
Methods of Employment Verification in the Mortgage Process
Mortgage lenders use a variety of methods to verify a borrower’s employment. The method selected will depend on the type of employment the applicant has, the documentation they provide, and the lender’s specific requirements. The following are the most common methods used by lenders to verify employment:
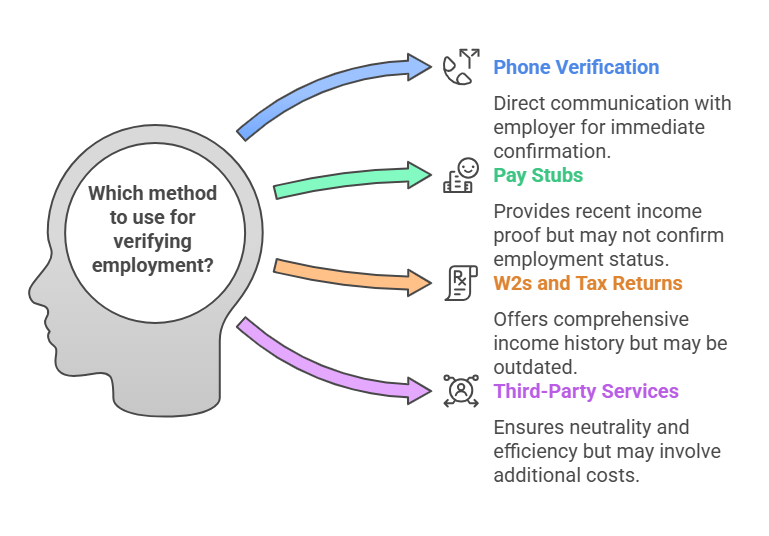
1. Phone Verification
Phone verification involves the lender contacting the applicant’s employer directly to confirm their employment status. This is one of the most reliable methods because it involves direct communication with a company representative who can provide real-time, accurate information.
Employers will typically verify basic employment details such as the applicant’s position, the length of their employment, and their income. This method is especially useful for confirming current employment and income, making it a commonly used method by many mortgage lenders.
Advantages:
- Direct and accurate communication with the employer.
- Quick and efficient, especially for simple verifications.
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming, as it depends on the availability of the employer or HR representative.
- Employers may not always be willing to provide employment verification information, especially if they have policies against releasing such details.
2. Pay Stubs
Applicants often provide pay stubs as part of the mortgage application process. Pay stubs are issued by employers on a regular basis (usually bi-weekly or monthly) and detail the applicant’s earnings, tax deductions, and other important financial information.
Mortgage lenders will request recent pay stubs to confirm the borrower’s current income level. This helps lenders ensure that the applicant earns enough to meet their monthly mortgage obligations.
Advantages:
- Easy for applicants to provide.
- Detailed information on earnings, taxes, and deductions.
Disadvantages:
- Pay stubs can be easily manipulated or falsified.
- They only show the applicant’s most recent income, which may not provide a full picture of their financial stability.
3. W2s and Tax Returns
For a more comprehensive look at an applicant’s income, lenders may request W2 forms and tax returns. These documents show the applicant’s annual earnings and provide a more long-term view of their income history. W2 forms summarize the total wages earned by an employee for the year, while tax returns provide a more detailed account of income, expenses, and tax liabilities.
This method is often used for applicants who have been employed for an extended period and have a consistent income. It’s also used to verify income for self-employed individuals.
Advantages:
- Provides a comprehensive overview of an applicant’s income over the past year.
- Harder to manipulate than pay stubs.
Disadvantages:
- May not reflect recent changes in income, such as a raise or a new job.
- Self-employed individuals may need to provide additional documentation, such as profit-and-loss statements or business tax returns.
4. Third-Party Verification Services
Many lenders rely on third-party verification services to confirm an applicant’s employment and income details. These services specialize in verifying employment history and income on behalf of the lender. Third-party services collect employment data from a variety of sources, including direct employer contact, payroll records, and government databases.
These services can be especially useful for applicants with unconventional employment histories, such as freelancers or self-employed individuals, as they can assist in gathering accurate and reliable documentation.
Advantages:
- Quick and reliable, especially for complex employment situations.
- Reduces the workload for both lenders and borrowers.
- Can verify employment across multiple employers and locations.
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than traditional verification methods.
- Some services may not be as customizable for unique employment situations.
Comparison Table: Employment Verification Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Phone Verification | High accuracy, direct communication with employer | Time-consuming, employer may not respond promptly |
| Pay Stubs | Easy to provide, detailed earnings breakdown | Can be falsified, does not show long-term stability |
| W2s and Tax Returns | Comprehensive income view, harder to manipulate | Does not reflect recent changes, not ideal for self-employed |
| Third-Party Verification | Reliable, saves time for both parties | More expensive, less customizable |
How Employment Verification Affects Your Mortgage Application
Employment verification plays a critical role in the mortgage application process. It helps lenders assess an applicant’s financial stability, confirms the accuracy of the applicant’s income, and ensures that they are capable of making consistent mortgage payments. In this part, we will explore the various ways employment verification influences mortgage applications, the role it plays in the loan approval process, and some common challenges that borrowers may face during this verification phase.
Why Mortgage Lenders Require Employment Verification
Mortgage lenders require employment verification to ensure they are lending money to borrowers who have the financial ability to repay their mortgage loan. The key reasons why lenders demand this verification include:
1. Confirming Income Stability
One of the primary reasons for employment verification is to confirm the borrower’s income stability. Lenders need to be sure that applicants have a steady, reliable source of income that will enable them to meet their mortgage obligations month after month. Without verifying income, lenders could be approving loans for individuals who may not be able to afford the home or meet their payment commitments.
For example, a borrower who has a full-time job with a steady income is seen as a lower-risk applicant compared to someone with a more erratic or unstable income stream. By ensuring that an applicant’s income is reliable and consistent, lenders can make better decisions about whether they should approve the loan or not.
2. Evaluating Borrower’s Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio
Employment verification helps mortgage lenders calculate the borrower’s debt-to-income (DTI) ratio. The DTI ratio compares the borrower’s monthly debt payments (including the projected mortgage) to their gross monthly income. This ratio is a significant factor in determining how much a borrower can afford in terms of monthly mortgage payments. The lower the DTI, the more favorable the application will be.
For instance, a borrower who earns $5,000 per month and has $1,500 in debt obligations will have a DTI ratio of 30%. A low DTI ratio suggests that the borrower has the financial capacity to make regular mortgage payments, whereas a high DTI ratio indicates that the borrower may struggle to manage additional financial obligations.
Employment verification is vital in accurately calculating this ratio, ensuring that lenders approve only those applicants who are financially capable of handling the mortgage payments without becoming financially strained.
3. Risk Mitigation for Lenders
Lenders use employment verification as a means to mitigate risk. If a borrower fails to disclose a job loss or inaccurate income information, the lender might approve a loan that the borrower is ultimately unable to repay. This could result in significant financial losses for the lender. Employment verification helps to minimize these risks by ensuring that the borrower’s income is as stated in their application.
The lender’s risk assessment is significantly influenced by the borrower’s employment history, especially when they are evaluating an applicant’s long-term employment stability. If an applicant has a history of job-hopping or is currently in a short-term or seasonal position, lenders may view them as higher-risk borrowers. Consistent employment with a reputable company, on the other hand, will enhance the applicant’s credibility in the eyes of the lender.
How Employment Verification Impacts the Loan Approval Process
The employment verification process directly impacts whether or not a borrower is approved for a mortgage. Here’s how it affects the loan approval process:
1. Verifying Income for Loan Amount Determination
The loan amount a borrower qualifies for is based on their ability to repay the mortgage. By verifying income, lenders determine the amount of money the borrower can afford to borrow. When employment verification confirms that the borrower has the required income, lenders can confidently calculate the loan amount, ensuring that the monthly payments align with the borrower’s financial capacity.
For example, if a borrower’s income is verified as $60,000 per year, the lender will use this information to assess how much of a mortgage the borrower can afford. This step involves factoring in the borrower’s existing debts and the proposed mortgage payments.
If discrepancies are found during the employment verification process—such as the borrower not having sufficient income or having debts that weren’t disclosed—it may result in a reduced loan offer, a higher interest rate, or even a loan denial.
2. Checking for Consistency in Employment History
Another aspect of the employment verification process is ensuring that the applicant’s employment history is accurate and consistent. Lenders typically verify job stability over a period of two years, as a longer-term employment history indicates a more reliable income source. Applicants with gaps in employment or frequent job changes may be seen as a riskier investment by lenders, as these factors suggest a lack of income stability.
The verification process may reveal discrepancies between the borrower’s application and the actual employment records. If a borrower has left out previous job information or misrepresented their employment status, this can delay or jeopardize the loan approval process.
3. Identifying Potential Red Flags
The employment verification process helps lenders identify potential red flags in the application. Red flags may include a sudden drop in income or inconsistent employment history, which could indicate that the borrower is having financial difficulties or that they may not be entirely truthful in their application. If these issues are detected during the verification process, the lender may request additional documentation or reconsider the loan application altogether.
In some cases, employment verification can uncover discrepancies such as unreported income, employment gaps, or inaccurate job titles. These inconsistencies can lead to the rejection of the loan application, delays in processing, or requests for further investigation into the applicant’s financial situation.
Common Challenges in Employment Verification
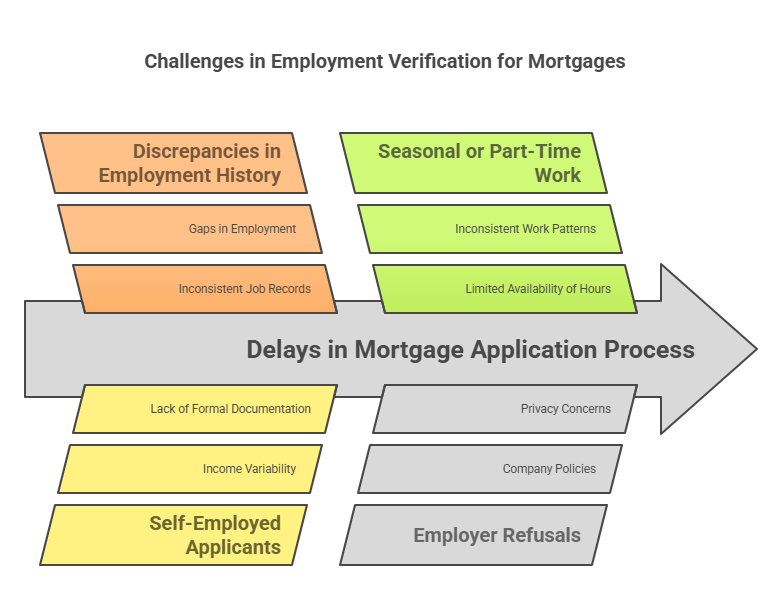
While employment verification is a standard part of the mortgage application process, borrowers can encounter challenges that delay or complicate the process. Some common challenges in employment verification include:
1. Discrepancies in Employment History
A common challenge during employment verification is discrepancies between the borrower’s application and the verification results. This may include differences in the length of time at a particular job, changes in job titles, or inconsistencies in income reporting. These discrepancies can delay the approval process and may require additional documentation or clarification from the borrower.
For example, if a borrower lists a previous job on their application but their employer confirms that they were never employed there, it could lead to questions about the accuracy of the entire application.
2. Self-Employed Applicants
Self-employed individuals often face additional challenges in the employment verification process. Unlike traditional employees who can provide pay stubs and W2 forms, self-employed borrowers may need to provide more extensive documentation, such as tax returns, profit-and-loss statements, and bank statements. Verifying the income of a self-employed individual is often more complicated and may involve additional steps to confirm their financial stability.
Lenders may require two years of tax returns and other documents to assess the applicant’s ability to repay the mortgage. This extra verification process may take longer than traditional employment verification, and self-employed borrowers may face more scrutiny during the approval process.
3. Seasonal or Part-Time Work
Applicants who work in seasonal or part-time jobs may also encounter challenges during the employment verification process. Lenders often prefer applicants with full-time, permanent employment, as it provides a more predictable and stable source of income. Applicants who rely on seasonal work or multiple part-time jobs may find it difficult to prove a consistent and reliable income stream.
Lenders will typically look for patterns in income over time, and applicants with inconsistent or fluctuating earnings may be viewed as a higher risk. In these cases, additional documentation or explanations may be required to convince the lender that the borrower can still afford the mortgage.
4. Employer Refusals to Provide Verification
Some employers may refuse to provide employment verification due to privacy concerns, company policy, or other reasons. This can create delays in the mortgage application process, as lenders may need to find alternative ways to verify employment. In these cases, borrowers may be asked to provide additional documentation, such as pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements, to support their application.
How Exact Background Checks Can Assist in Employment Verification
In some cases, the employment verification process can become more complicated, especially for self-employed individuals or those with a non-traditional work history. Exact Background Checks can help simplify and streamline this process by providing accurate, efficient employment verification services. Exact Background Checks works with both lenders and applicants to ensure timely and accurate verification of employment, income, and job history, regardless of the applicant’s employment situation.
Exact Background Checks offers a comprehensive service that includes third-party verification and other methods of employment confirmation. Their services help minimize errors, reduce delays, and ensure the verification process is completed swiftly, allowing borrowers to move forward with their mortgage applications without unnecessary obstacles.
Legal Aspects of Employment Verification for Mortgages
While employment verification is crucial in the mortgage process, it must be conducted in compliance with legal standards to protect both the applicant and the lender. Various laws and regulations govern how employment verification is conducted during the mortgage application process, ensuring that the rights of applicants are protected while providing lenders with the information needed to assess loan eligibility.
Fair Lending Laws
Fair Lending Laws, such as the Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA) and the Home Mortgage Disclosure Act (HMDA), prohibit discrimination in lending practices. These laws ensure that all individuals, regardless of race, gender, religion, or other protected categories, have equal access to mortgage loans. When verifying employment, lenders must be careful not to base decisions on discriminatory factors unrelated to a borrower’s ability to repay the loan.
Employment verification cannot be used as a tool to discriminate against applicants with non-traditional employment histories (e.g., self-employed individuals, seasonal workers) unless the applicant’s income stability is called into question by a legitimate verification process. Lenders must ensure they are following these laws to avoid legal ramifications.
Privacy and Consent
Privacy laws play a crucial role in employment verification. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) requires lenders and third-party verification agencies to obtain the applicant’s written consent before initiating any employment verification. This consent allows the lender or verification service to access personal and employment information, including details about the applicant’s income and employment history.
Applicants have the right to be informed about the purpose of the verification, and the data collected must only be used for that specific purpose. Failure to obtain proper consent or using the information for unauthorized purposes can lead to legal consequences, including penalties or lawsuits.
Lenders must also ensure that personal data is securely handled and protected throughout the verification process. Sensitive information, such as salary details, job history, and personal identifiers, must be stored and transmitted in compliance with data protection regulations to avoid data breaches and potential misuse.
Data Protection and Security
With the rise of digital recordkeeping and third-party verification services, ensuring the security of personal information during the employment verification process has become more important than ever. Employment verification companies and lenders must comply with stringent data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or similar regulations in other jurisdictions, to ensure that applicants’ personal data is not compromised.
Lenders are required to adopt robust security protocols, including encryption, secure servers, and strict access controls, to protect the privacy of applicants throughout the employment verification process. Any breach of data protection can lead to significant legal liabilities and reputational damage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Employment Verification for Mortgages
To provide further clarity on the topic of employment verification for mortgages, here are some of the most frequently asked questions along with detailed answers:
Why do lenders require employment verification for mortgages?
Lenders use VOE to confirm that an applicant has stable income and employment history, which helps them assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan.
How does a lender verify my employment for a mortgage?
Lenders typically verify employment by contacting the employer directly, using written verification letters, or employing automated third-party services.
What documents are needed for employment verification during a mortgage application?
Common documents include pay stubs, W-2 forms, tax returns, and sometimes a formal letter from the employer confirming employment and income details.
Can I get a mortgage if I’m self-employed?
Yes, but self-employed applicants typically need to provide additional documentation, such as tax returns and business financial statements, to verify income.
What happens if my employment verification doesn’t match my application?
If there are discrepancies, the lender may require additional clarification or documentation. In some cases, it may lead to a loan denial.
Why do lenders require employment verification for mortgages?
Lenders use VOE to confirm that an applicant has stable income and employment history, which helps them assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan.
How does a lender verify my employment for a mortgage?
Lenders typically verify employment by contacting the employer directly, using written verification letters, or employing automated third-party services.
What documents are needed for employment verification during a mortgage application?
Common documents include pay stubs, W-2 forms, tax returns, and sometimes a formal letter from the employer confirming employment and income details.
Can I get a mortgage if I’m self-employed?
Yes, but self-employed applicants typically need to provide additional documentation, such as tax returns and business financial statements, to verify income.
What happens if my employment verification doesn’t match my application?
If there are discrepancies, the lender may require additional clarification or documentation. In some cases, it may lead to a loan denial.
Conclusion: The Importance of Employment Verification for Mortgages
In conclusion, employment verification is an essential aspect of the mortgage application process. It provides lenders with the necessary information to evaluate the borrower’s ability to repay the loan and helps ensure the financial stability of the borrower. The employment verification process plays a critical role in determining the loan amount, interest rate, and overall loan approval, making it a significant factor in the home-buying process.
Understanding the legal aspects of employment verification is important for both lenders and borrowers to ensure compliance with laws protecting the borrower’s privacy and rights. From fair lending practices to data protection, maintaining transparency and security during the verification process is crucial.
For borrowers, understanding the role of employment verification and knowing how to prepare for it can significantly reduce delays and increase the likelihood of mortgage approval. Utilizing services like Exact Background Checks can simplify the verification process and ensure that all employment information is accurate, timely, and compliant with legal standards.
Whether you are applying for a mortgage, working with a lender, or managing employment verification for a client, it is essential to have a reliable, trustworthy process in place. Exact Background Checks is a trusted partner that can help streamline employment verification for mortgage applications, ensuring that both borrowers and lenders can navigate the process smoothly.