Key Components of a Risk Mitigation Plan

Introduction to Risk Mitigation Plans: What Are They and Why Are They Important?
A risk mitigation plan is a critical component of effective risk management for businesses, organizations, and even individuals. It outlines the strategies and actions needed to identify, assess, and reduce or eliminate potential risks that could disrupt operations, cause financial losses, damage reputation, or impact growth. In today’s unpredictable business environment, having a well-thought-out risk mitigation plan is essential for ensuring business continuity, safeguarding assets, and maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
What Is a Risk Mitigation Plan?
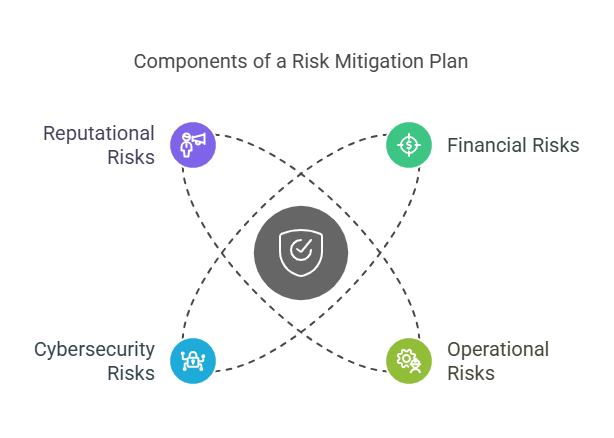
A risk mitigation plan is a proactive approach to identifying, assessing, and addressing potential risks that could negatively affect an organization’s operations. It involves implementing strategies to reduce the likelihood of these risks occurring or minimizing their impact if they do occur. These plans can be applied across various types of risks, such as financial, operational, cybersecurity, and reputational risks.
The primary goal of a risk mitigation plan is to create a structured approach for dealing with potential threats, ensuring that businesses can react effectively when an unforeseen event arises. By carefully planning and preparing for various risks, organizations can better safeguard their assets, protect their reputation, and ensure smoother business operations.
Why Is a Risk Mitigation Plan Essential for Businesses?
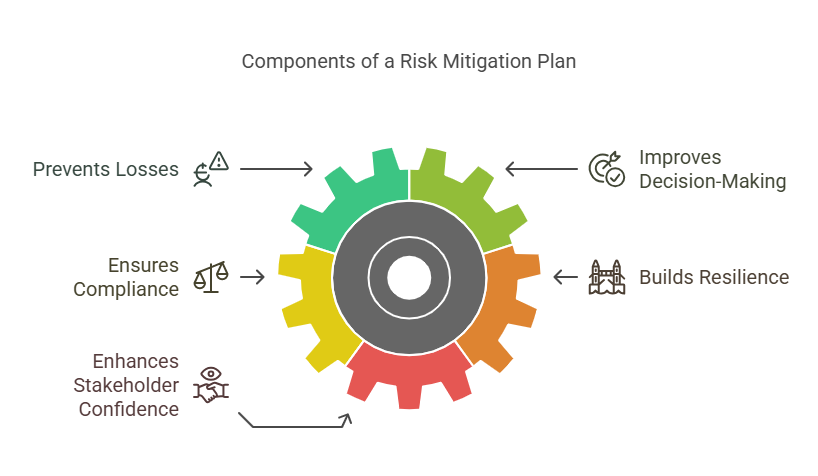
Developing a risk mitigation plan is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevents Losses: By identifying and mitigating risks before they become problematic, businesses can avoid financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
- Improves Decision-Making: A well-defined plan helps businesses make informed decisions about investments, resource allocation, and future strategies, knowing the potential risks and rewards.
- Ensures Compliance: For organizations in highly regulated industries, having a risk mitigation plan in place is essential to meet compliance requirements and avoid legal penalties.
- Builds Resilience: Risk mitigation helps businesses remain resilient in the face of unexpected challenges, whether they are financial crises, cybersecurity breaches, or natural disasters.
- Enhances Stakeholder Confidence: Investors, customers, and employees are more likely to trust businesses that have a comprehensive risk mitigation plan in place, knowing that the organization is well-prepared to handle potential risks.
The Process of Developing a Risk Mitigation Plan
Developing a risk mitigation plan involves a series of steps aimed at systematically identifying and addressing risks. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Risk Identification: The first step is identifying all potential risks that could impact the organization. These risks could stem from various sources, including internal operations, external market conditions, legal and regulatory changes, and more.
- Risk Assessment: After identifying risks, businesses assess the likelihood and potential impact of each risk. This helps prioritize which risks need to be addressed first based on their severity.
- Risk Mitigation: This step involves designing strategies and solutions to either eliminate or reduce the impact of the identified risks. Strategies could include risk avoidance, risk transfer (e.g., insurance), risk reduction, or risk acceptance.
- Monitoring and Review: A risk mitigation plan must be continuously monitored to ensure its effectiveness. This includes regular reviews and updates to account for new risks or changes in the business environment.
Types of Risks Businesses Commonly Face
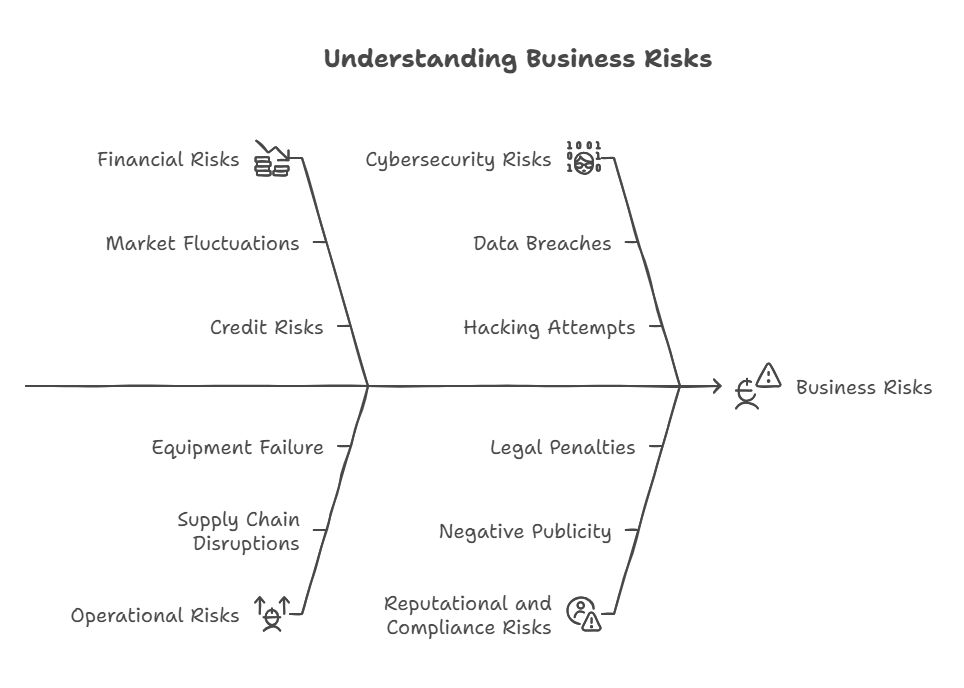
Businesses face a variety of risks, each requiring specific mitigation strategies. Here are some of the most common types of risks that companies may need to address through a risk mitigation plan:
- Financial Risks: These include risks related to revenue generation, liquidity, investments, and credit. Fluctuations in market conditions, interest rates, or foreign exchange can create financial uncertainty.
- Operational Risks: These are risks arising from day-to-day business operations. They may include supply chain disruptions, equipment failure, and workforce issues.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As businesses increasingly rely on digital platforms, cybersecurity has become a major concern. Cyberattacks, data breaches, and hacking attempts can result in significant financial and reputational damage.
- Reputational Risks: Damage to a company’s reputation can have long-lasting effects, especially in the age of social media. Negative publicity, poor customer service, or scandals can lead to a loss of trust among stakeholders.
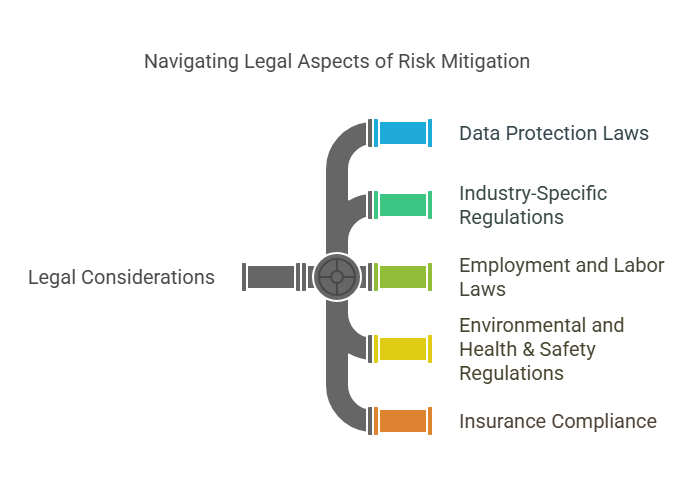
- Compliance and Legal Risks: These include the risks associated with failing to comply with local, national, or international regulations and laws. For example, non-compliance with data protection laws like GDPR or financial regulations like SOX can lead to legal penalties.
Benefits of Implementing a Risk Mitigation Plan
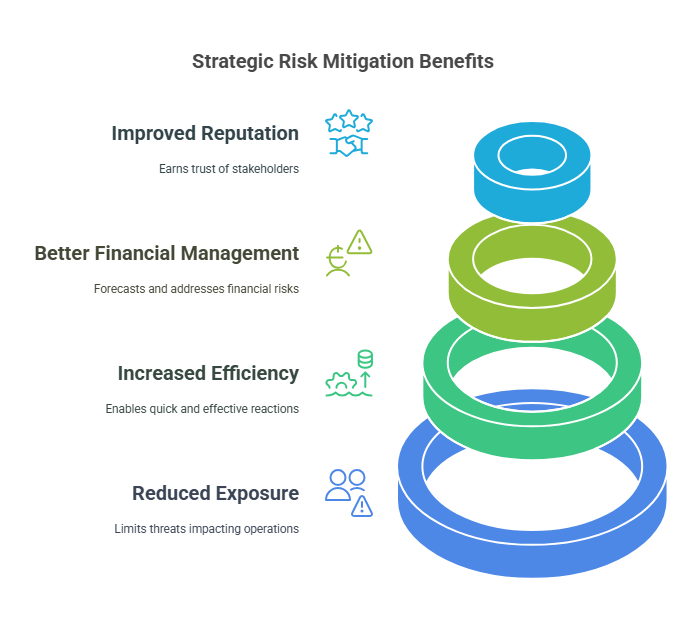
A risk mitigation plan provides numerous benefits for organizations, making it a crucial part of strategic planning. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Reduced Exposure to Risk: By identifying and addressing potential risks, businesses can limit their exposure to threats that could negatively impact operations.
- Increased Efficiency: Having a clear plan for managing risks allows businesses to react more quickly and effectively, reducing downtime and resource waste.
- Better Financial Management: A risk mitigation plan helps businesses avoid costly mistakes by forecasting potential financial risks and addressing them proactively.
- Improved Reputation: Organizations that demonstrate a commitment to risk management are more likely to earn the trust of customers, investors, and regulators.
In the next section, we will explore the specific components of a risk mitigation plan and what it might include to address various risks effectively.
Key Components of a Risk Mitigation Plan: What It Might Include
When creating a risk mitigation plan, it’s important to incorporate several key components that work together to identify, assess, and reduce potential risks. These elements help ensure that risks are managed in a structured way, and that businesses are prepared to act when necessary.
1. Risk Identification
Risk identification is the process of pinpointing potential risks that could negatively impact an organization. Risks can be external (e.g., economic downturns or natural disasters) or internal (e.g., system failures or employee misconduct). Common methods for identifying risks include:
- Risk workshops and brainstorming sessions involving key stakeholders across the organization.
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) to identify both internal and external risks.
- Risk audits to assess past incidents and identify recurring risks.
2. Risk Assessment
Once risks are identified, businesses need to assess them to determine their potential impact and likelihood. Risk assessment helps prioritize risks based on their severity, guiding businesses on where to focus their mitigation efforts. Key elements of risk assessment include:
- Likelihood: How probable is the risk to occur?
- Impact: If the risk does occur, what would be the consequences for the business?
- Risk Matrix: A tool used to map the likelihood and impact of risks, helping businesses prioritize which risks need immediate attention.
3. Mitigation Strategies
Once the risks are assessed, mitigation strategies are developed to either reduce or eliminate the impact of identified risks. Different strategies might be used depending on the type of risk:
- Risk Avoidance: Changing plans or processes to avoid potential risks. For example, a company might decide to stop entering high-risk markets to avoid exposure to financial risk.
- Risk Reduction: Implementing measures to reduce the severity of a risk, such as improving cybersecurity to reduce the chances of a data breach.
- Risk Transfer: Transferring the risk to another party, such as purchasing insurance or outsourcing certain operations to a third-party vendor.
- Risk Acceptance: Acknowledging that some risks are unavoidable and setting aside resources to handle the consequences if they occur.
4. Monitoring and Review
Risk mitigation is an ongoing process. Businesses must continuously monitor and review their risks and the effectiveness of their mitigation strategies. This can include:
- Regular risk audits and reviews to ensure that the mitigation plan is working.
- Continuous monitoring of risk factors, such as market trends or cybersecurity threats.
- Updating the risk mitigation plan as new risks emerge or business conditions change.
Employment Screening as Part of Risk Mitigation: ExactBackgroundChecks.com
A key element of a risk mitigation plan for many businesses involves managing employment-related risks. One effective way to do this is by using background checks and employment screening services, such as those offered by ExactBackgroundChecks.com.
ExactBackgroundChecks.com helps businesses mitigate risks related to hiring by providing comprehensive background checks. These services can help identify potential risks related to employee fraud, criminal behavior, or non-compliance with industry regulations. By thoroughly vetting candidates, businesses can minimize risks related to workplace misconduct and maintain a safer, more reliable workforce.