Ways to Dispute a False Positive Drug Test

How to Dispute a False Positive Drug Test
A false positive drug test occurs when a screening test inaccurately identifies the presence of drugs or prohibited substances in a person’s system. This means the test suggests drug use when the individual has not consumed the substance in question. While drug testing technologies have advanced significantly, no testing method is perfect, and errors can occur for a variety of reasons.
False positive results are particularly concerning because they can lead to serious personal and professional consequences. For this reason, understanding the nature of false positives, their causes, and their impact is crucial, especially for individuals undergoing workplace drug testing, legal proceedings, or medical evaluations.
Common Causes of False Positives
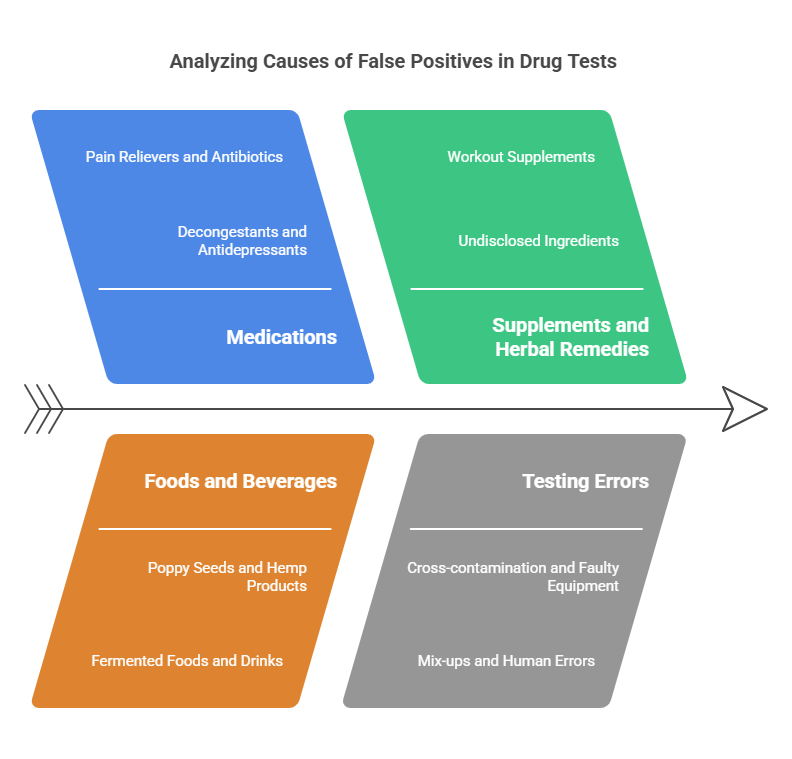
False positives may arise from numerous sources, often unrelated to actual drug use. The most common causes include:
1. Medications
Certain over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications can interfere with drug tests, resulting in false positives. Examples include:
- Decongestants: Many cold and flu medications contain pseudoephedrine, a compound that can mimic amphetamines in urine drug tests.
- Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as sertraline (Zoloft), may produce false positives for benzodiazepines.
- Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen and naproxen are anti-inflammatory drugs that have been linked to false positives for THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the psychoactive component of marijuana.
- Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics, such as rifampin and fluoroquinolones, can occasionally interfere with drug test results.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Medications used to treat acid reflux, like omeprazole, may trigger false positives for THC.
2. Foods and Beverages
Everyday foods and drinks can also influence drug test outcomes. Some examples include:
- Poppy Seeds: Consuming baked goods containing poppy seeds can lead to a false positive for opiates. While poppy seeds themselves are not drugs, they can contain trace amounts of morphine or codeine.
- Hemp Products: Certain hemp-derived products, such as oils, protein powders, and snacks, may contain trace amounts of THC, enough to produce a positive result in sensitive tests.
- Fermented Foods and Drinks: Kombucha, a fermented tea, contains small amounts of alcohol that could potentially cause a false positive in alcohol testing.
3. Supplements and Herbal Remedies
Dietary supplements and herbal remedies are not always tightly regulated, and some may contain undisclosed ingredients that mimic the chemical structure of prohibited substances. This is particularly true for workout supplements marketed for weight loss or energy boosts.
4. Testing Errors
Human or procedural errors during the testing process can also lead to false positives. Examples include:
- Cross-contamination: Samples can become contaminated if not handled or stored properly.
- Faulty Equipment: Outdated or improperly calibrated testing equipment may yield inaccurate results.
- Mix-ups: Clerical errors, such as mislabeled samples, can cause individuals to be incorrectly identified as having failed a drug test.
5. Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions can interfere with drug test results. For example:
- Diabetes: Individuals with poorly controlled diabetes may have elevated ketone levels, which can lead to false positives for alcohol.
- Kidney Disease or Liver Disease: Impaired organ function can cause the body to produce metabolites that resemble certain drugs in chemical structure.
How Drug Tests Work
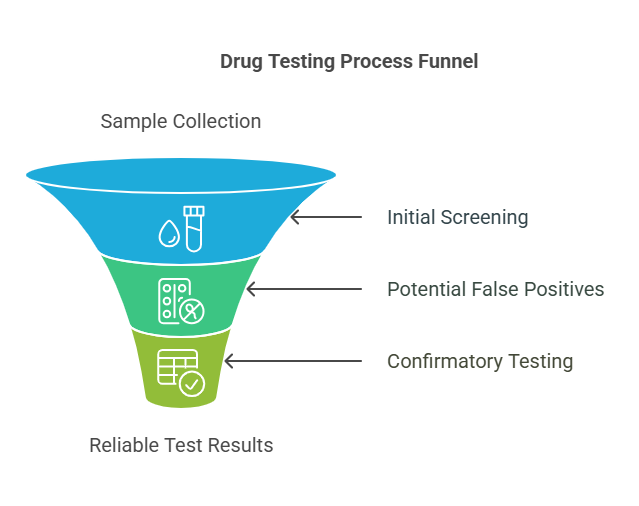
To understand why false positives occur, it helps to know how drug tests operate. The two primary types of drug tests are:
- Initial Screening Tests: These are often immunoassay tests, designed to detect specific drug metabolites in a sample (e.g., urine, blood, hair, or saliva). Immunoassay tests are fast, inexpensive, and widely used but can produce false positives due to their sensitivity to substances with similar chemical structures.
- Confirmatory Tests: If the initial test is positive, a more precise method, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), is used to confirm the result. Confirmatory tests are highly accurate and less prone to error but are more expensive and time-consuming.
Understanding the differences between these tests can help individuals advocate for themselves if they receive a false positive result.
Consequences of a False Positive Result
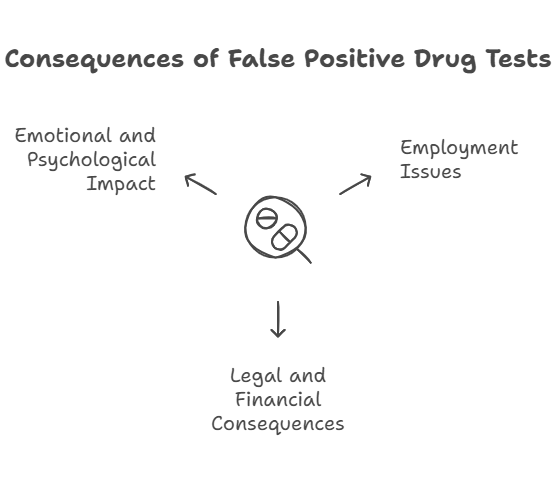
The consequences of a false positive drug test can be severe, affecting various aspects of an individual’s life. Some of the most significant impacts include:
1. Employment Issues
- Job Loss: For individuals subjected to random drug testing at work, a false positive could lead to immediate termination, particularly in industries with strict drug-free workplace policies, such as transportation, healthcare, and law enforcement.
- Missed Opportunities: A failed pre-employment drug test may disqualify a candidate from being hired, even if the result is later proven inaccurate.
2. Legal and Financial Consequences
- Probation Violations: A false positive drug test could lead to penalties for individuals on probation or parole, including extended supervision or incarceration.
- Custody Battles: In family law cases, a failed drug test might jeopardize parental rights, even if the result is eventually disputed.
- Financial Losses: Disputing a false positive often involves costs such as legal fees, medical consultations, and retesting.
3. Emotional and Psychological Impact
- Stress and Anxiety: Receiving a false positive result can be an emotionally taxing experience, particularly when trying to prove one\u2019s innocence.
- Reputational Damage: Even when proven false, the stigma associated with a failed drug test can harm personal relationships and professional networks.
The Importance of Understanding False Positives
False positive drug tests highlight the importance of accurate testing methods and the need for due process when handling disputed results. For employers, ensuring the reliability of testing procedures protects both the company and its employees from unnecessary harm. For individuals, awareness of the factors contributing to false positives empowers them to take proactive steps in disputing erroneous results.
By recognizing the potential causes of false positives and their implications, individuals can better prepare themselves to navigate the dispute process. The next step involves learning how to effectively challenge a false positive drug test result, which will be detailed in the subsequent section.
Steps to Dispute a False Positive Drug Test
A false positive drug test can have serious consequences, but disputing it effectively can mitigate potential damage to your reputation, career, or legal standing. The process requires a systematic approach, from identifying the root cause of the false positive to ensuring a fair resolution. Below is a step-by-step guide to disputing a false positive drug test, along with actionable tips to protect yourself.
Step 1: Stay Calm and Review Your Rights
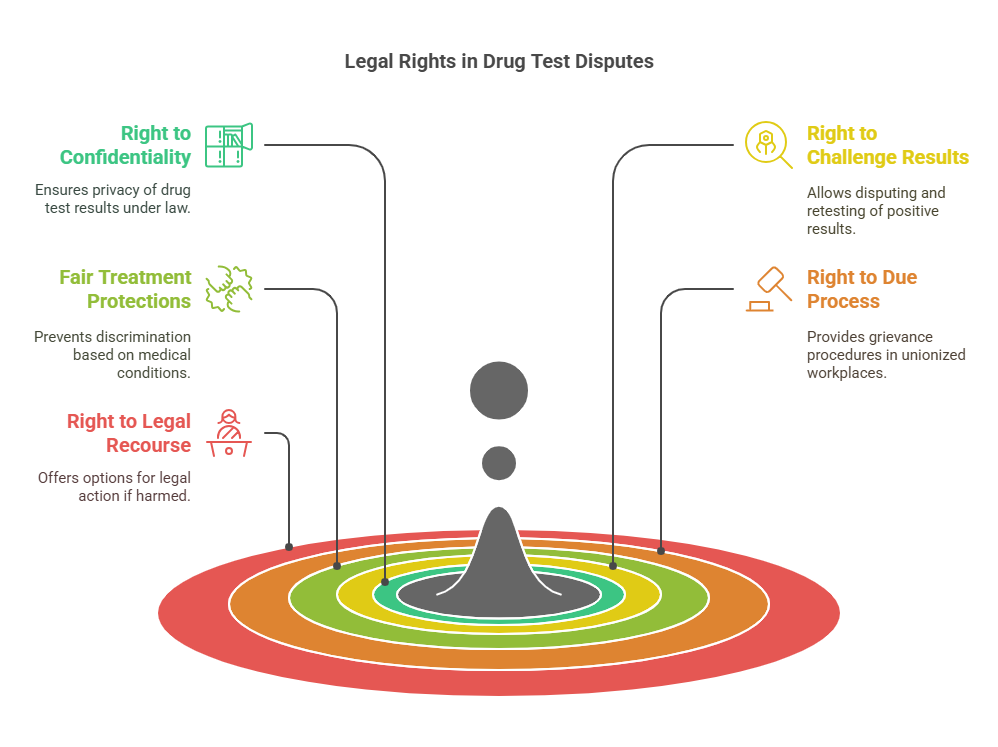
When faced with a false positive drug test, it’s natural to feel anxious or defensive. However, staying calm and composed is crucial. Start by understanding your legal and workplace rights, which may include:
- The Right to a Retest: Many employers or organizations allow for a secondary test (confirmation test) to verify the initial result.
- Access to Test Details: You have the right to request documentation about the test, including the type of test used, the laboratory that conducted it, and the specific substances detected.
- Confidentiality Protections: Drug test results are typically protected under privacy laws, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), preventing unauthorized disclosure.
Take the time to familiarize yourself with your employer’s drug testing policies or the guidelines relevant to the situation (e.g., probation terms or legal requirements).
Step 2: Request a Retest or Confirmation Test
Initial screening tests, often immunoassays, are prone to false positives because they are highly sensitive to substances with similar chemical structures. A confirmation test, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), provides more accurate results. Follow these steps to request a retest:
- Act Quickly: Request the retest as soon as you are notified of the positive result. Many organizations have strict time limits for retesting.\n2. Verify the Sample’s Chain of Custody: Ensure that your original sample has been properly stored and handled to prevent contamination or degradation.\n3. Pay for the Retest if Necessary: Some employers may require you to cover the cost of the retest. While this may seem unfair, it’s worth the expense to clear your name.
If the retest comes back negative, it will typically override the initial positive result.
Step 3: Consult a Medical Review Officer (MRO)
A Medical Review Officer (MRO) is a licensed physician trained to evaluate drug test results and determine if there are legitimate medical explanations for a positive result. Employers often involve an MRO as part of the testing process, but you can also request an independent MRO evaluation.
Provide the MRO with:
- A list of all medications, supplements, and over-the-counter products you were taking before the test.
- Any relevant medical records or prescriptions that support your case.
- Details about recent dietary habits, such as consuming poppy seeds or hemp products.
The MRO will review this information alongside your test results and may contact the laboratory for further clarification.
Step 4: Verify the Laboratory’s Testing Procedures
Laboratory errors are a common cause of false positives. To ensure the validity of your test, you can request information about the laboratory’s procedures, including:
- Equipment Calibration: Confirm that the testing equipment was properly maintained and calibrated.\n- Quality Control Measures: Check if the lab follows standardized quality control protocols, such as those outlined by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) or the College of American Pathologists (CAP).\n- Sample Handling: Ensure that the chain of custody was strictly followed to prevent sample mix-ups or contamination.
You can also request an independent laboratory to retest your sample if you suspect errors in the original testing process.
Step 5: Gather Supporting Evidence
Building a strong case to dispute a false positive requires gathering evidence that supports your claim. This may include:\n
- Documentation of Medications and Supplements: Compile a list of all substances you were using, along with receipts or prescriptions.\n2. Medical Records: Provide records from your doctor that explain any medical conditions or treatments that could have influenced the test result.\n3. Dietary Logs: Note any foods or beverages consumed before the test, such as poppy seeds or kombucha.\n4. Witness Statements: If applicable, gather statements from coworkers, friends, or family members who can attest to your character and behavior.
Presenting this evidence to your employer, legal counsel, or the testing authority can strengthen your case.
Step 6: Seek Legal Assistance if Necessary
If your employer or the testing authority refuses to overturn the false positive result despite clear evidence, you may need to seek legal help. An attorney specializing in employment law or drug testing disputes can assist with:
- Negotiating with Your Employer: Your lawyer can advocate for you and work toward a resolution, such as reinstatement or clearing your record.\n- Filing a Complaint: In cases of procedural errors or discrimination, your attorney can help file a complaint with regulatory bodies, such as the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).\n- Pursuing Legal Action: If the false positive has caused significant harm, you may have grounds for a lawsuit to recover damages.
Legal assistance is especially important in cases involving wrongful termination, probation violations, or child custody disputes.
Step 7: Communicate with Your Employer or Testing Authority
Clear and professional communication is essential when disputing a false positive drug test. Follow these tips:\n
- Be Honest: Provide accurate information about your medical history, dietary habits, and substance use.\n- Stay Professional: Avoid accusatory language or emotional outbursts when discussing the situation.\n- Follow Procedures: Adhere to any dispute resolution processes outlined in your employer\u2019s drug testing policy.
If possible, request a meeting with the relevant decision-makers to explain your case and present your evidence.
Step 8: Use Professional Background Screening Services
Organizations like Exact Background Checks play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy of employment screening processes. They use advanced testing methods and thorough verification procedures to minimize the risk of false positives. Exact Background Checks provides services such as:\n
- Reliable Drug Testing: Utilizing certified laboratories and state-of-the-art testing technology to ensure accurate results.\n- Comprehensive Reviews: Employing Medical Review Officers (MROs) to evaluate drug test results and identify potential false positives.\n- Employee Support: Offering resources to help employees understand their rights and dispute erroneous results.
Employers who partner with reputable background screening companies demonstrate their commitment to fairness and accuracy in the workplace.
Step 9: Educate Yourself to Prevent Future Issues
Preventing future false positives requires proactive steps, such as:\n
- Reading Labels: Check the ingredients of medications, supplements, and foods for substances that may interfere with drug tests.\n- Informing Test Administrators: Before taking a drug test, disclose any medications or health conditions that could affect the results.\n- Maintaining Records: Keep detailed records of prescriptions, medical treatments, and dietary habits as evidence in case of disputes.
By taking these precautions, you can reduce the likelihood of encountering false positives in the future.