Factors That Affect Federal Background Check Duration

Introduction to Federal Background Checks and Timeline Factors
Federal background checks are a crucial part of the employment process, especially for positions that involve access to sensitive information, national security concerns, or roles that require a higher level of trust. Whether it’s for government jobs, law enforcement positions, or industries subject to federal regulations, understanding the timeframes and factors involved in federal background checks is essential for both employers and job applicants.
This section will provide a comprehensive introduction to what a federal background check entails, why it is necessary for certain positions, and what factors affect the time it takes to complete the process. We will also explore the typical processing times for different types of federal background checks and discuss the factors that can influence these timelines.
What is a Federal Background Check?
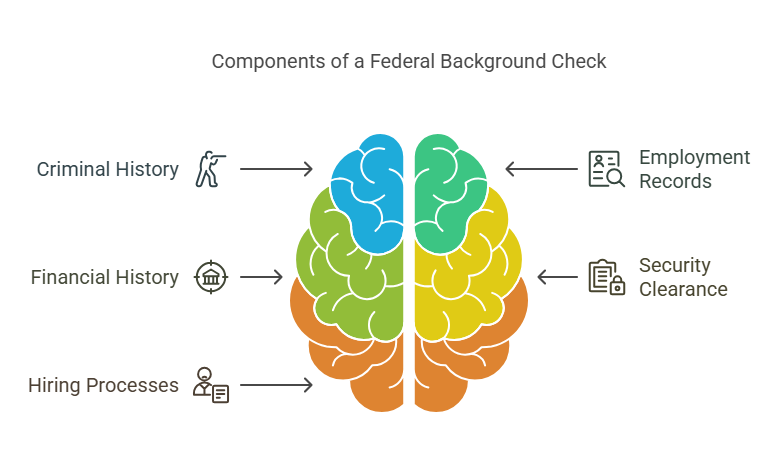
A federal background check is a process used to verify an individual’s criminal history, employment records, financial history, and other personal information at the national level. Unlike state or local background checks, which focus only on a specific jurisdiction, federal background checks provide a broader, more comprehensive look into an individual’s history across the entire country. These checks are often required for positions that involve federal contracts, access to classified information, or roles that could pose a security risk if the wrong person is hired.
Federal background checks are a key component of security clearance procedures and are also frequently used in the hiring process for government jobs or jobs involving national security. However, they are not just limited to government roles. Many employers in industries such as defense, healthcare, and finance may require federal background checks as part of the hiring process.
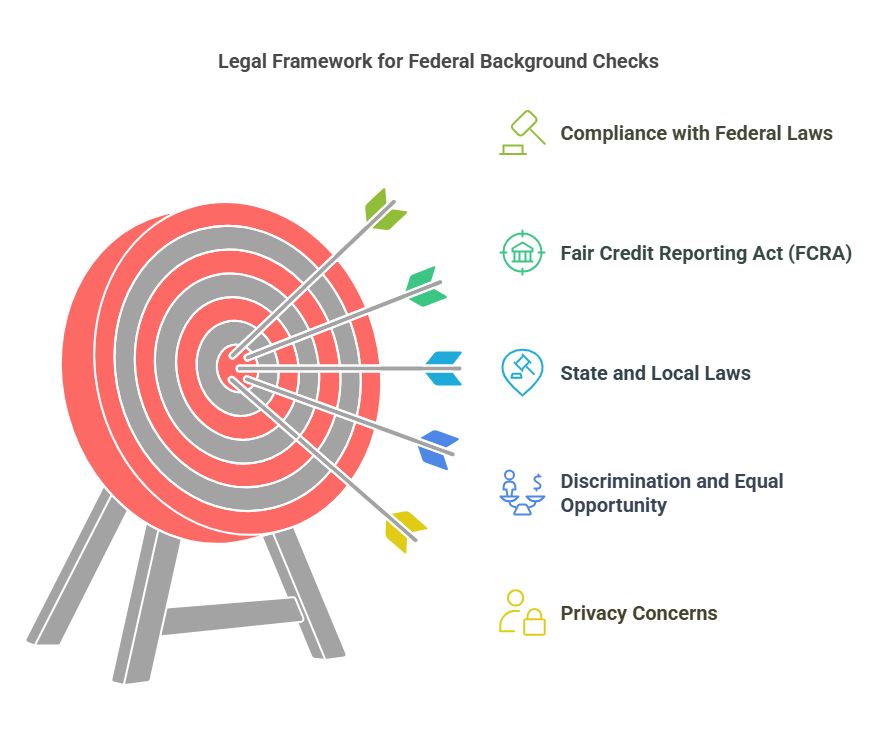
Why are Federal Background Checks Important?
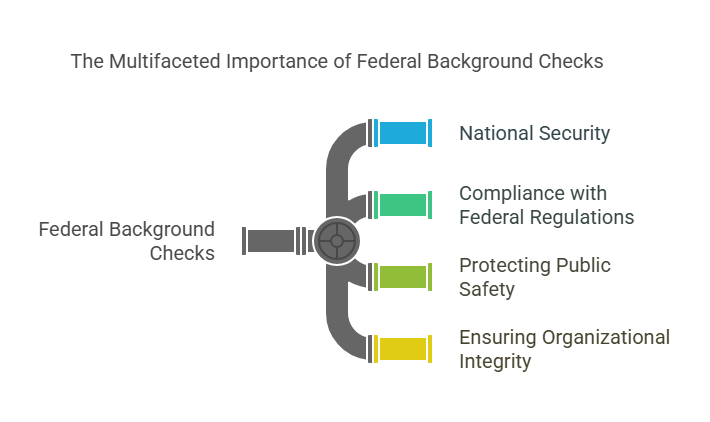
Federal background checks are essential for several reasons:
- National Security: For roles that require access to classified information or national security data, a federal background check ensures that the individual can be trusted with sensitive information. This is especially critical in fields such as defense contracting, law enforcement, intelligence, and government positions.
- Compliance with Federal Regulations: Certain industries are required by law to conduct federal background checks to ensure that their employees meet specific standards. For example, employers in healthcare, transportation, and finance often must ensure that their employees do not have criminal backgrounds that would disqualify them from certain roles.
- Protecting Public Safety: Federal background checks help mitigate the risk of hiring individuals who might pose a risk to public safety, whether it involves criminal activity, financial mismanagement, or other disqualifying factors.
- Ensuring Organizational Integrity: Companies that handle sensitive data or work with federal agencies must conduct federal background checks to maintain the integrity and trustworthiness of their workforce.
How Does a Federal Background Check Differ from State or Local Background Checks?
While state or local background checks focus only on records within a specific jurisdiction, a federal background check casts a much wider net. Federal checks include:
- National Criminal History Review: A federal background check accesses databases such as the FBI’s National Crime Information Center (NCIC), which includes records for crimes that fall under federal jurisdiction, such as drug trafficking, immigration offenses, or federal fraud cases.
- Fingerprinting: Some federal background checks, especially those for security clearances or law enforcement positions, may require fingerprinting to confirm an individual’s identity and to cross-check with federal criminal databases.
- Security Clearances: For certain jobs, a federal background check may also involve additional screenings for security clearance, which includes a review of financial history, personal interviews, and other in-depth investigations into the individual’s suitability for a sensitive role.
- Employment History and Financial Checks: While local or state checks may only verify employment history within that region, federal checks can look at a nationwide employment record and check for any federal offenses or violations that could affect an individual’s eligibility for a specific role.
The key distinction is that federal checks offer a more extensive review, one that includes not only criminal history but also a comprehensive look at an individual’s background at the national level.
Factors That Influence the Time it Takes for a Federal Background Check
Several factors can impact the timeline for a federal background check. While each case is unique, understanding these factors will help applicants and employers manage expectations and ensure that the process is as smooth as possible.
1. Type of Federal Background Check
The type of federal background check being conducted will have a significant impact on how long it takes to process. There are several different kinds of checks, and each comes with its own set of requirements. Some of the common types of federal background checks include:
- Criminal History Checks (FBI): These checks verify an individual’s criminal history at the federal level. They are usually processed relatively quickly, typically within 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the volume of requests.
- Fingerprint-Based Checks: If fingerprints are required, the processing time may increase due to the time it takes to send the prints to the FBI or another relevant agency and to have them cross-checked with federal databases. These checks can take anywhere from 3 to 6 weeks, but delays are possible, especially if the prints are not legible or if the FBI’s records are unclear.
- Security Clearance Checks: For roles that require a security clearance, the background check is much more extensive. This process can involve interviews, financial checks, and a detailed review of an individual’s entire history. For high-level clearances, such as Top Secret, this can take anywhere from several months to over a year to complete, depending on the complexity of the investigation.
2. Volume of Requests
The volume of background check requests being processed at the time can impact the time it takes to complete a federal background check. If there is a high demand for checks—such as during busy hiring seasons or when a large government contract is in place—the backlog of requests can lead to delays.
Federal agencies such as the FBI handle a significant number of background check requests annually, and during peak periods, there may be longer processing times due to the increased demand for these services.
3. Accuracy and Completeness of Information
The accuracy of the personal information provided for the background check plays a significant role in how quickly the process can move forward. Incomplete or inaccurate information, such as misspelled names, incorrect dates of birth, or mismatched social security numbers, can delay the process while corrections are made.
Fingerprint-based checks are especially sensitive to accuracy; if the fingerprints are not legible or are improperly submitted, they may need to be resubmitted, resulting in additional delays.
4. The Complexity of the Individual’s Background
If an individual has a complex or lengthy background, such as multiple criminal offenses, legal issues, or international travel history, the process may take longer as investigators may need additional time to collect and verify information from various sources. For example, international criminal checks or reviews of foreign employment may add time to the overall process.
In cases where security clearance is required, the investigation may include detailed interviews with the individual, their family, friends, and colleagues, which could add several months to the process.
Typical Processing Times for Federal Background Checks
While every federal background check is unique, there are general timelines that can be expected depending on the type of check. Here’s a summary of the typical processing times:
- FBI Criminal History Check: 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the volume of requests and whether fingerprinting is required.
- Fingerprint-Based Checks: 3 to 6 weeks (electronic submission), though paper submissions may take up to 8 weeks.
- Security Clearance Checks: Several months to a year, particularly for high-level clearances such as Top Secret or SCI (Sensitive Compartmented Information) clearances.
Process and Tools for Conducting Federal Background Checks
Types of Federal Background Checks
Before delving into the process itself, it’s important to understand that there are various types of federal background checks. The type of check determines the steps involved, the level of scrutiny, and the time required to complete it. Here are some of the most common types of federal background checks:
1. FBI Criminal History Check
An FBI criminal history check is one of the most common types of federal background checks. It typically involves submitting fingerprints to the FBI for a check against its National Crime Information Center (NCIC) database. This type of background check verifies whether an individual has any criminal convictions, arrests, or pending charges at the federal level.
- Step 1: The individual submits their fingerprints (electronically or on paper) along with identifying information.
- Step 2: The FBI compares the fingerprints and information with records in their criminal database.
- Step 3: The FBI generates a report detailing any criminal history that matches the submitted fingerprints.
2. FBI Fingerprint-Based Checks
Fingerprint-based checks are another form of federal background checks, often required for roles that involve sensitive information, law enforcement positions, or national security clearances. Fingerprints are a unique identifier, and cross-referencing fingerprints with criminal records ensures the accuracy of the check.
- Step 1: Fingerprints are collected through an ink-based or electronic fingerprinting system.
- Step 2: The fingerprints are submitted to the FBI, either electronically or through traditional methods.
- Step 3: The FBI runs the fingerprints through its database to identify any criminal history or discrepancies.
- Step 4: A report is generated, which may include criminal convictions, open investigations, or records related to national security violations.
3. Security Clearance Checks
Federal positions that require access to classified or sensitive information necessitate a more in-depth background investigation. A security clearance check may involve criminal history checks, financial history, interviews with acquaintances, and a detailed review of the individual’s background over several years. The level of clearance (Confidential, Secret, or Top Secret) will determine the depth of the investigation.
- Step 1: The individual completes a security clearance application, detailing their personal, professional, and financial history.
- Step 2: The federal government, typically through agencies like the Department of Defense or the Office of Personnel Management, begins the background investigation.
- Step 3: Investigators may interview the individual’s associates, review their financial history, and evaluate other factors that could impact security risks.
- Step 4: The information is reviewed to determine the individual’s eligibility for security clearance.
4. Employment History and Financial Checks
For certain positions, a federal background check may include reviewing employment history, educational records, and financial stability. While these checks may not always be as time-consuming as criminal history checks or security clearance checks, they are still important in determining an applicant’s suitability for certain positions.
Step-by-Step Process for Conducting a Federal Background Check
The process for conducting a federal background check can vary depending on the type of check being performed. However, there are several key steps that are common across most federal checks. Below is a general overview of the steps involved in conducting a federal background check:
Step 1: Submit the Required Information
The first step in the process is to submit the necessary information for the background check. This typically includes:
- Personal Details: Full name, date of birth, Social Security number (SSN), and other identifying information.
- Fingerprints: For FBI criminal history and fingerprint-based checks, fingerprints are required. These may be collected electronically or on paper at authorized fingerprinting locations.
- Consent: Applicants must consent to the background check and authorize the release of their records.
Step 2: Information Verification
Once the required information is submitted, the next step is verification. This involves checking the provided information against federal databases, such as the NCIC, to identify any discrepancies or criminal history.
For fingerprint-based checks, the submitted fingerprints are processed and cross-referenced with the FBI’s records. If there are no matches, the process is typically faster. However, if there is a match, further investigation may be required.
Step 3: Processing the Information
After the information is verified, the relevant federal agency or authority processes the background check. This can involve searching national criminal databases, reviewing employment records, or conducting interviews for security clearance purposes. The complexity of the background check will determine how long this step takes.
- Criminal History Checks: These are typically processed relatively quickly, especially if there are no matches or if the criminal history is limited.
- Security Clearance: These checks are more involved and can take several months due to the in-depth investigation required.
Step 4: Generation of the Report
Once the information has been processed, a report is generated. This report contains details about the individual’s criminal history, employment records, financial background, or security clearance eligibility.
- FBI Criminal History Report: This report outlines any criminal convictions or records related to the applicant’s national criminal history.
- Security Clearance Report: This includes an in-depth review of the applicant’s background, including interviews, financial assessments, and national security checks.
Step 5: Review and Decision
Once the background check report has been generated, it is reviewed by the employer, government agency, or security clearance board. The decision will depend on the findings in the report. If the report reveals no disqualifying issues, the individual may proceed with the job or clearance process. However, if red flags appear, further investigation or a denial of the application may occur.
Tools and Services for Federal Background Checks
While the federal background check process may seem straightforward, it can be complex and time-consuming, especially when conducted manually. Fortunately, there are several tools and services that can help streamline the process and ensure accurate, timely results.
Exact Background Checks
Exact Background Checks is a trusted service provider that specializes in conducting federal background checks for employers and individuals. Their platform allows businesses to efficiently conduct criminal history checks, employment verification, and security clearance background checks.
Key benefits of using Exact Background Checks include:
- Fast Processing Times: With a network of partners and streamlined workflows, Exact Background Checks can expedite the process of conducting federal background checks, reducing delays and ensuring timely hiring decisions.
- Comprehensive Reports: Exact Background Checks provides thorough, reliable reports that include criminal history, employment records, and additional checks such as security clearances.
- Compliance: Exact Background Checks ensures that all checks are conducted in compliance with relevant federal and state laws, including the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) and other privacy regulations.
- User-Friendly Interface: The platform is easy to use, allowing employers to initiate background checks, track progress, and receive completed reports quickly.
Other Federal Background Check Tools
There are several other services and tools available for conducting federal background checks. These include:
| Service Provider | Features | Average Processing Time | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exact Background Checks | Comprehensive criminal history checks, security clearance, employment history, fast processing, compliance with FCRA | 2 to 6 weeks | Varies |
| Accurate Now | Criminal checks, drug testing, employment verification, credit checks | 1 to 3 weeks | Varies |
| First Advantage | Criminal background checks, credit reports, education verification, drug testing | 2 to 4 weeks | Varies |
| Sterling Talent Solutions | Global background checks, fingerprint-based checks, I-9 verification | 3 to 6 weeks | Varies |